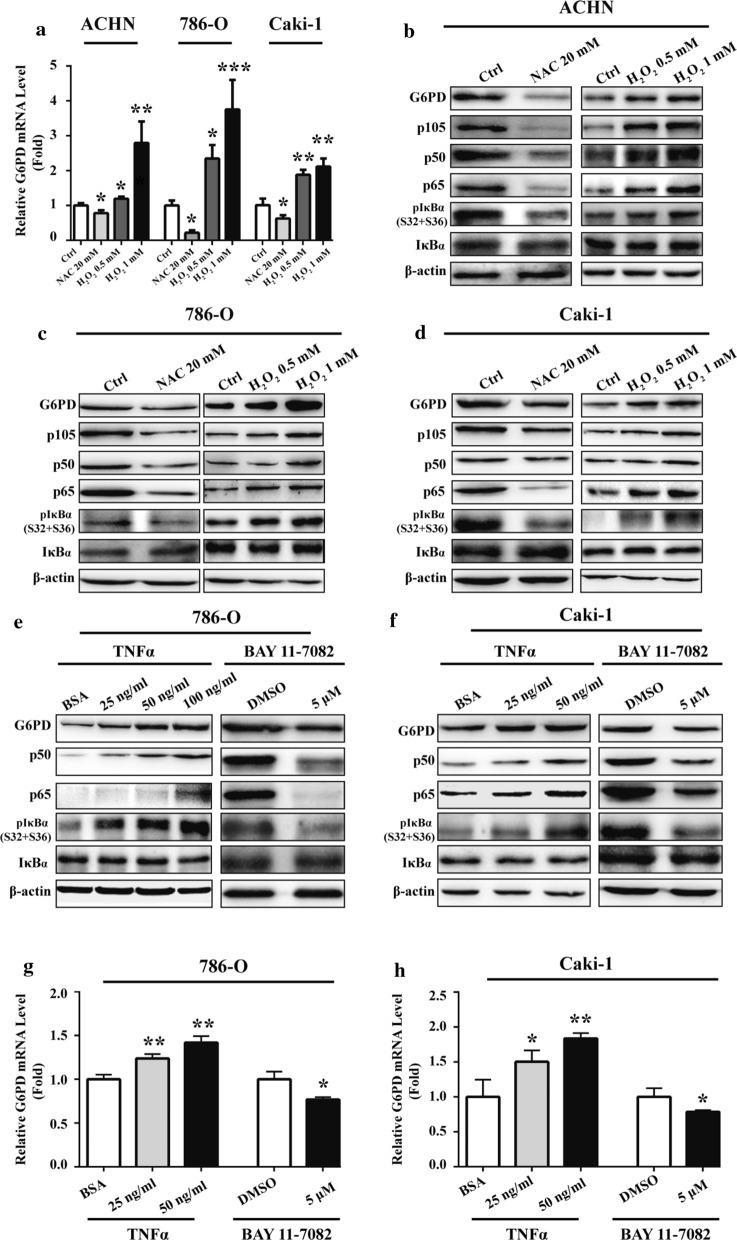
Fig. 1.
ROS positively regulated G6PD and NF-κB signaling pathway in ccRCC cells. a–d ACHN, 786-O or Caki-1 cells were treated with NAC (24 h) or H2O2 (2 h) to inhibit or induce ROS production, respectively. The changes in the expression of G6PD at the mRNA level and G6PD, p105, p50, p65, pIκBα, and IκBα at the protein level were detected using real-time RT-PCR (a, b) and Western blot (c, d) analysis, respectively. e–h 786-O or Caki-1 cells were treated with TNFα (24 h) or BAY11-7082 (24 h) at indicated doses to stimulate or inhibit NF-κB signaling pathway activities. The changes in the expression of G6PD, p50, p65, pIκBα, and IκBα at the protein level and G6PD at the mRNA level were detected using Western blot (e, f) and real-time RT-PCR (g, h) analysis, respectively. β-Actin was used as a loading control. Bars represent the mean ± SD from three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs each control