Fig. 7.
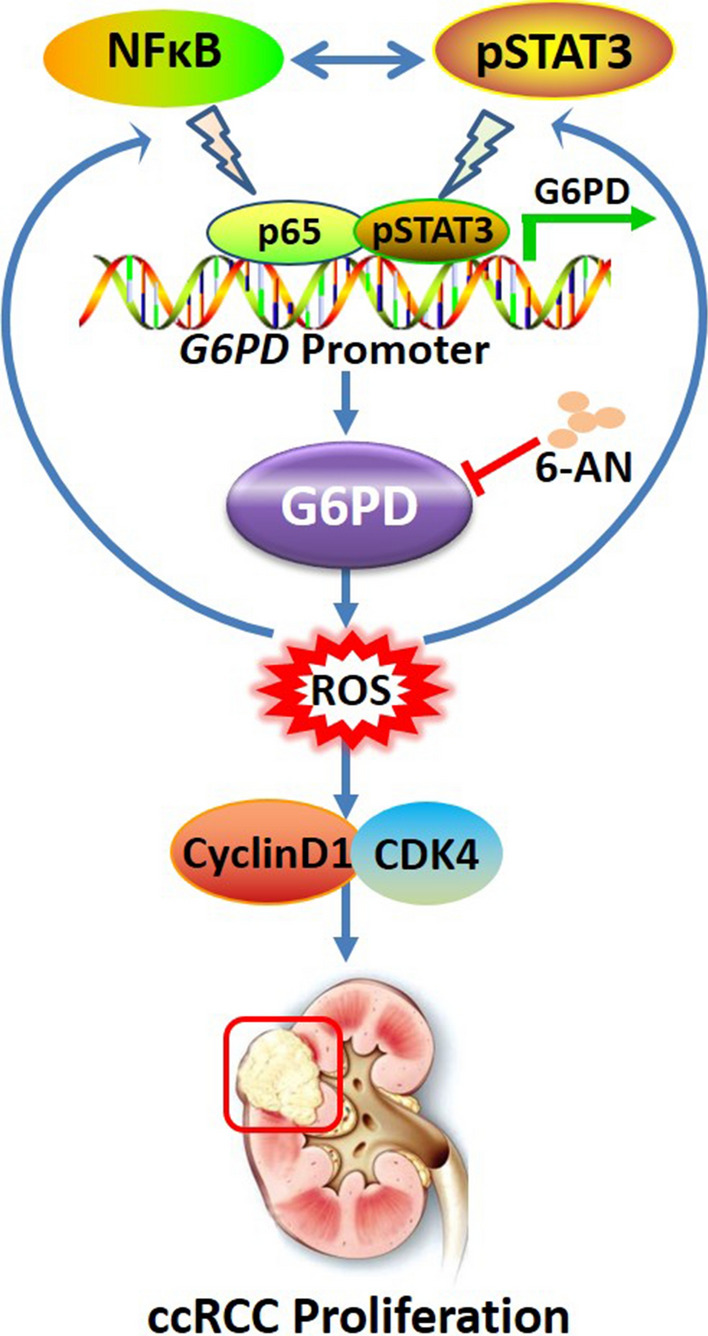
NF-κB and pSTAT3 synergistically drove G6PD overexpression and facilitated sensitivity to G6PD inhibition in ccRCC. ROS-stimulated NF-κB and pSTAT3 signaling over-activation could activate each other, and perform a cross-talk in the process of G6PD transcriptional regulation. The underlying mechanism was that p65 and pSTAT3 formed a p65/pSTAT3 complex, occupied the pSTAT3-binding site on the G6PD promoter, synergistically facilitated G6PD overexpression, and contributed to ccRCC proliferation. Moreover, G6PD activity inhibition might be a potential therapeutic strategy for ccRCC treatment
