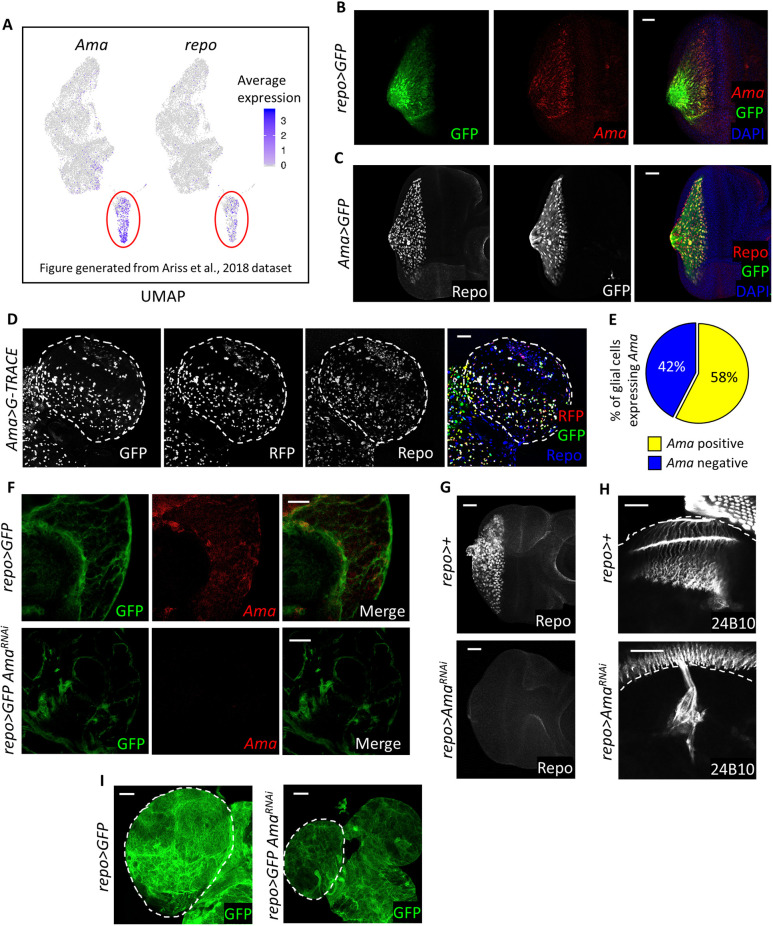
Fig. 1.
Ama is expressed in glia and is required in glial development. (A) Feature plots displaying the expression of genes on the UMAP clusters of a previously published third-instar eye disc scRNA-seq dataset (Ariss et al., 2018), showing that Ama and repo are co-expressed in the same cluster. (B) FISH for Ama mRNA in the eye disc showing expression in glial cells with glial membranes labeled by GFP. Final genotype: repo>mCD8GFP. (C) Repo immunofluorescence in the eye disc displaying expression in Ama-positive cells labeled by GFP. (D) Repo immunofluorescence in the third-instar brain (dashed outline) of Ama>G-TRACE showing the lineage and real-time expression of Ama-Gal4. GFP labels the lineage, whereas RFP represents the real-time expression. (E) Pie chart outlying the percentage of glial cells expressing Ama. Z-stacks of Ama>G-TRACE brains were counted. Data represent means of three experiments (Table S8). (F) FISH for Ama mRNA in the brain showing that there is expression in glial cells, with glial membranes labeled by GFP. Knockdown of Ama in glia results in loss of the FISH signal. Final genotypes: repo>mCD8GFP (top panel) repo>mCD8GFP AmaRNAi (bottom panel). (G) Repo immunofluorescence shows the lack of glia in the eye disc following Ama depletion. (H) Immunofluorescence using 24B10 antibody to label photoreceptor axons indicates defects in axons guidance in repo>AmaRNAi. The dashed lines indicate the outline of the brain. (I) Brains (outlined by dashed lines) are smaller in repo>AmaRNAi than in repo>GFP. GFP labels glial cell membranes. Final genotypes: repo>mCD8GFP (left panel) repo>mCD8GFP AmaRNAi (right panel). Scale bars: 20 µm.