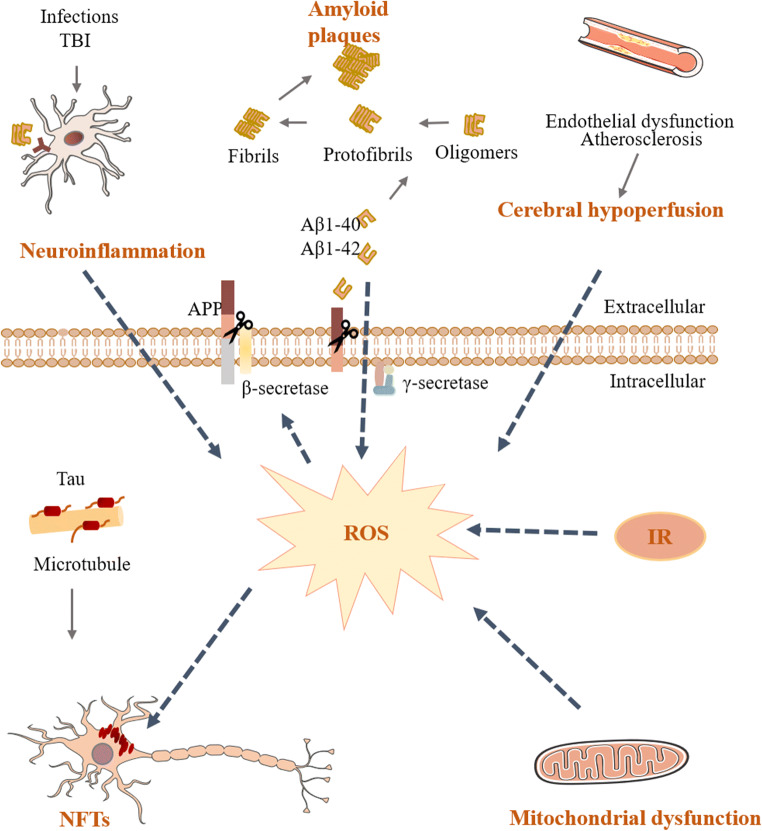
Fig. 1.
Key factors in the pathogenesis of AD. amyloid plaques and intracellular NFTs, neuroinflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, OS, IR, and chronic cerebral hypoperfusion are the main causes of AD development. These factors are related to each other directly or indirectly. Cerebral hypoperfusion due to advanced atherosclerosis or endothelial dysfunction, IR, and mitochondrial dysfunction lead to an elevation in ROS levels which results in overexpression and increased processing of APP, hyperphosphorylation of tau, and NFT pathology leading to neuronal death. Aβ, TBI, and infections are some of the factors that can elicit inflammation. Abbreviations: Aβ amyloid-beta, AD Alzheimer’s disease, APP amyloid precursor protein, IR insulin resistance, NFT neurofibrillary tangle, OS oxidative stress, ROS reactive oxygen species, TBI traumatic brain injury