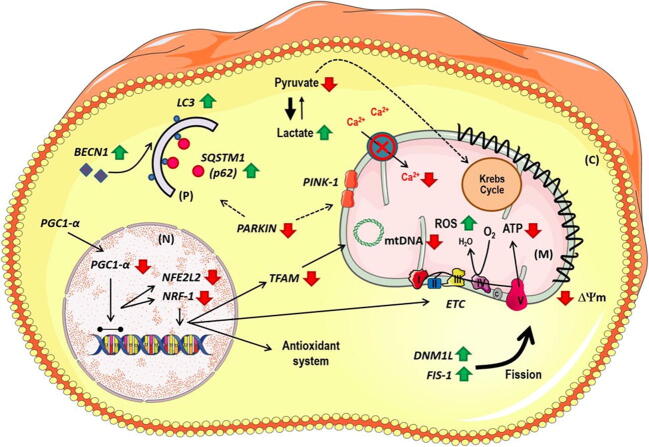
Fig. 6.
Schematic representation of mitochondrial deregulation observed in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from ALS patients. Cells from ALS patients present mitochondrial depolarization and diminishment in mitochondrial calcium uptake and/or retention, changes in redox homeostasis, and a decrease in metabolism biogenesis–related gene expression, namely, PGC-1α, NFE2L, NRF1, TFAM, and tRNAleu. Moreover, PBMCs from ALS individuals show an augmentation in mitochondrial fission (represented by an increase in DNM1L and FIS-1 expression) and a reduction in mitochondrial degradation signaling since there is a significant decrease in PARKIN expression. Notwithstanding, there is a significant increase in autophagy-related genes, as BECLIN, LC3, and SQSTM1. All these changes can further contribute to the decreased levels of ATP production and pyruvate in ALS PBMCs, and the augmented lactate levels observed in patients’ cells