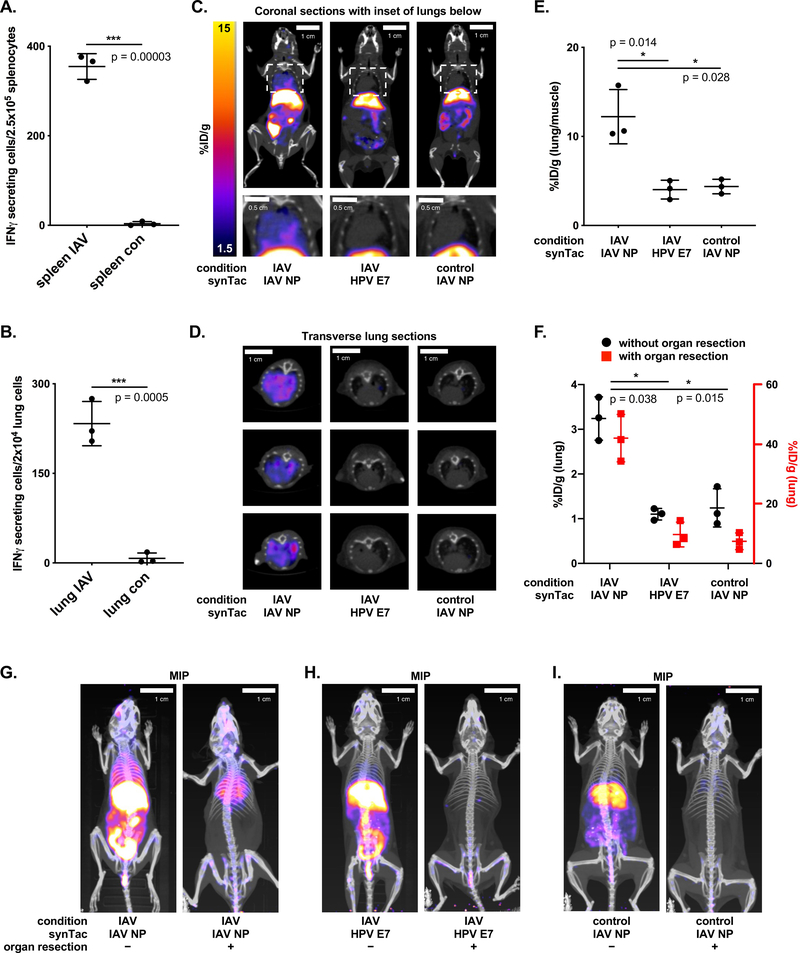
Figure 5.
PET-CT imaging with the IAV NP synTac. Non-tumor bearing C57BL/6 mice were infected with IAV via nasal drip 9 days prior to analysis of IAV NP-specific CD8 T cells. A-B) ELISpot analysis of IAV NP-specific CD8 T cell responses in the spleens (A) and lungs (B) of IAV-infected or uninfected control mice (means ± SD are shown; n = 3/group; ***p < 0.001; two-sided Student’s t-test). C-D) Coronal (C; full body top and close-up of lungs bottom) and transverse (D) PET-CT images of IAV-infected mice retro-orbitally injected with 64Cu-labeled IAV NP synTac (left) or 64Cu-labeled HPV E7 synTac (middle) 9 days after IAV infection. Uninfected control mice were imaged with the 64Cu-labeled IAV NP synTac (right). E) Quantification of 64Cu-labeled IAV NP synTac PET signal in the lungs of IAV-infected or control mice over background signal (hindleg muscle). Mice were injected with 64Cu-labeled IAV NP synTac 8 days after IAV infection and PET-CT scanning was performed the next day (9 days after infection). IAV-infected mice were also given the 64Cu-labeled HPV E7 synTac in which the PET signal in the lungs was similar to that observed in uninfected mice (means ± SD are shown; n = 3/group; *p <0.05). F) Quantification of synTac PET signals in the lungs before (black) and after (red) abdominal organ resection. The function of the red axis (right) is to show the value of the signal in the lungs after organ resection and coordinates with the red points in the graph. IAV-infected mice were injected with 64Cu-labeled IAV NP or HPV E7 synTac 8 days after IAV infection and PET-CT imaging was performed the next day (9 days after infection). Uninfected control mice were given the 64Cu-labeled IAV NP synTac (means ± SD are shown; n = 3/group; *p <0.05). G-I) PET-CT imaging with synTacs before (left) and after (right) abdominal organ resection. IAV-infected mice were injected with 64Cu-labeled IAV NP synTac (G) or 64Cu-labeled HPV E7 synTac (H) 8 days after IAV infection and PET-CT imaging was performed the next day (9 days after infection). I) Uninfected control mice were imaged with the 64Cu-labeled IAV NP synTac. Shown are representative MIP PET-CT images of the same mice before (left) and after (right) abdominal organ resection (n = 3/group).