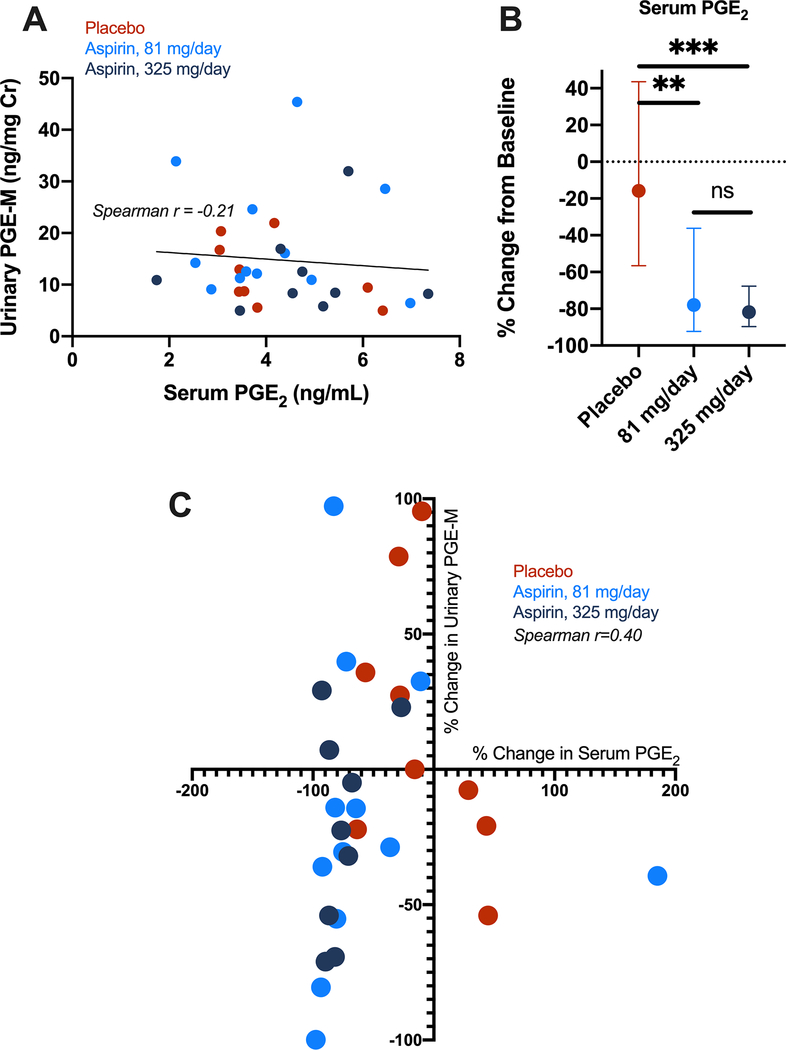
Figure 4.
PGE2 measurement in serum of ASPIRED participants. A) Spearman correlation of baseline urinary PGE-M (systemic) and serum PGE2 (circulating) demonstrates measures are not well correlated. B) Aspirin intervention with 81 or 325 mg/day significantly reduces serum PGE2 from baseline compared to placebo. Mann-Whitney test, **p<0.01; ***p <0.001; ns = not significant. C) The percent decrease in urinary PGE-M, is modestly correlated with the percent change in serum PGE2 following aspirin intervention. Spearman r = 0.40; one-tailed p-value = 0.035.