Figure 2.
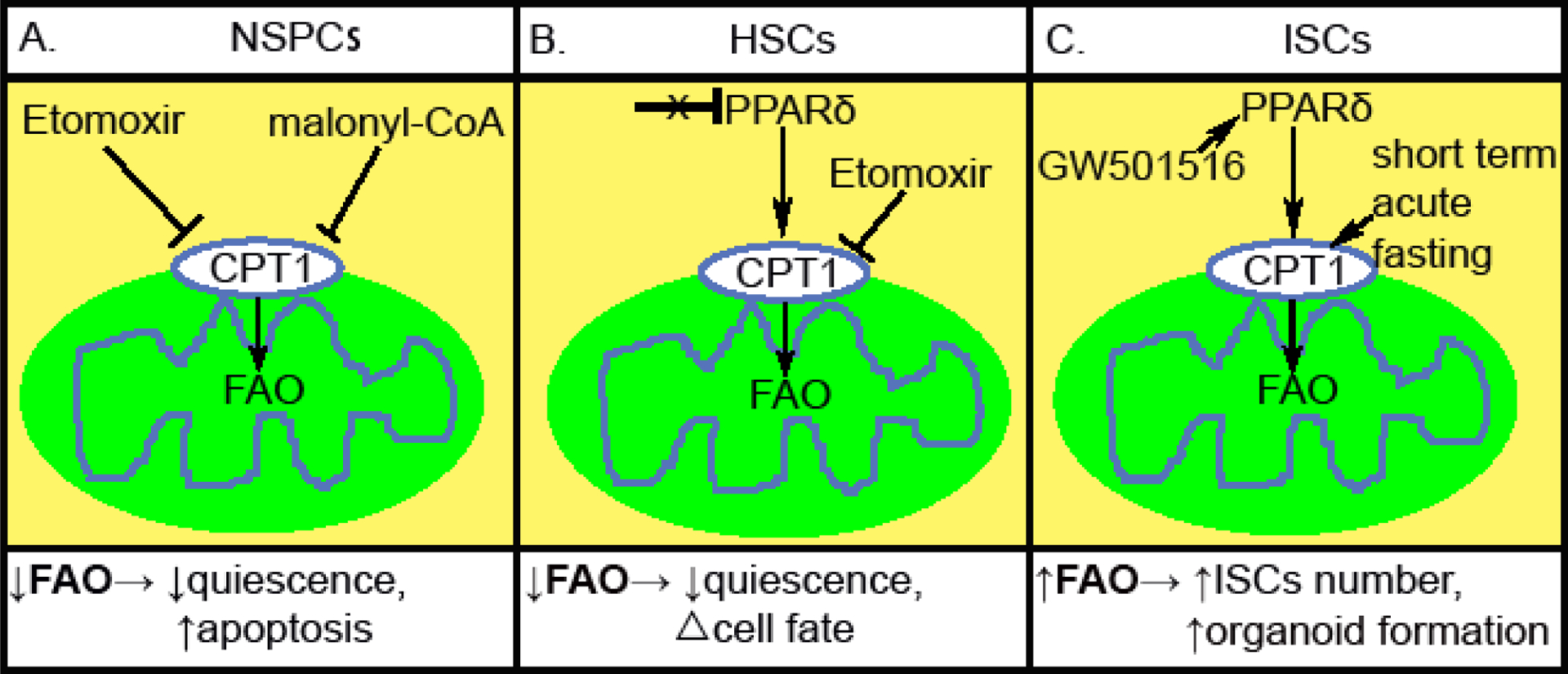
Modulating fatty acid oxidation (FAO) impacts tissue-specific stem cell function. (A) Inhibiting CPT1 by either Etomoxir or malonyl-CoA lead to decreased FAO in NSPCs, leading to reduced quiescence and increased apoptosis. (B) Inactivation of PPARδ or inhibiting CPT1 by Etomoxir lead to reduction of FAO in HSCs. This triggers an exit from quiescence and an alteration in symmetric versus asymmetric commitment. (C) Short term acute fasting or GW501516 treatment leads to activation of FAO in ISCs, and a subsequent increase in crypt Lgr5+ and Olfm4+ ISC/early progenitors, as well as crypt organoid-forming capacity.
