Figure 2: SPANX depletion induces G1/S arrest.
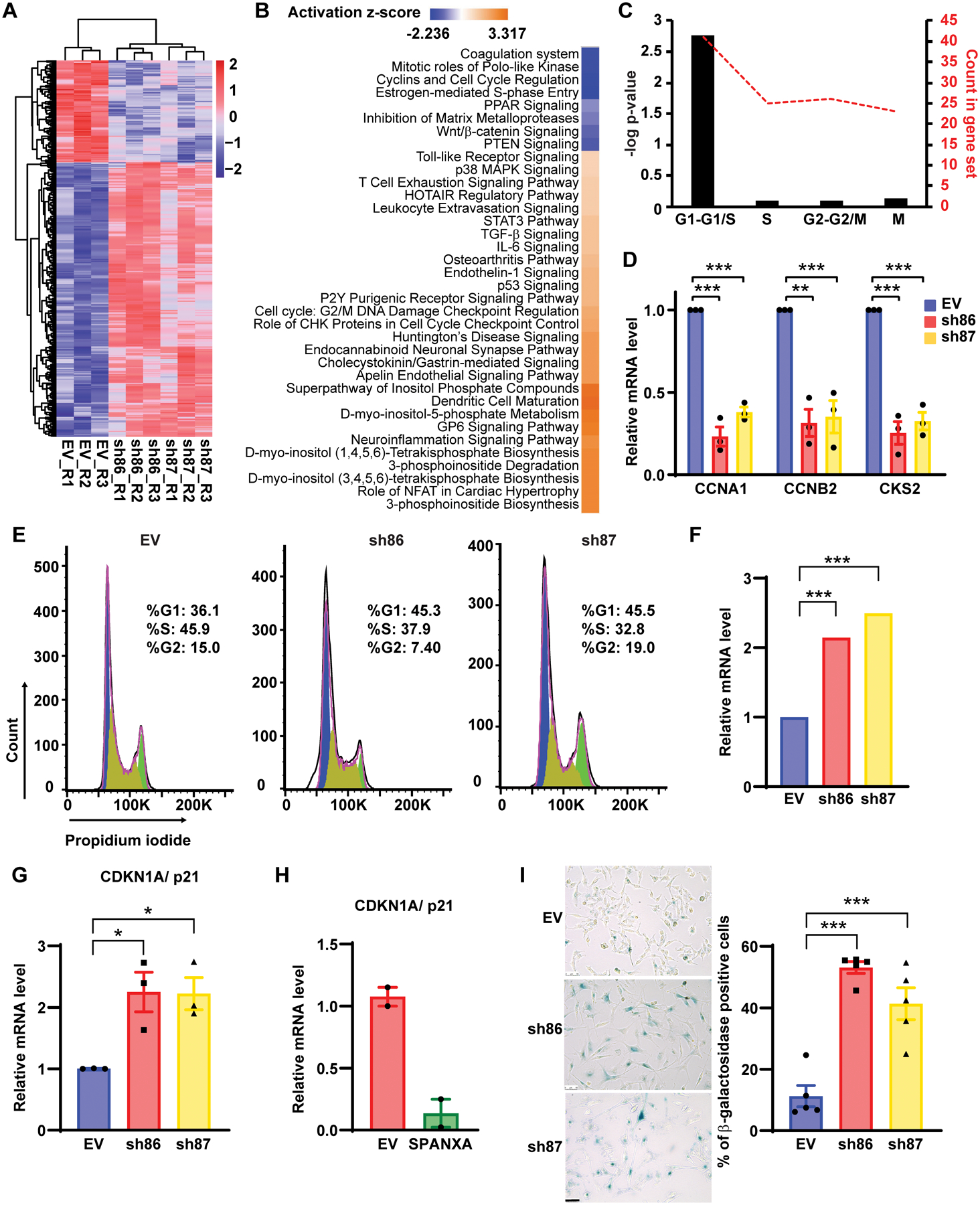
A. Heat map representing RNAseq data in A375 cells transduced with EV or SPANX-targeting shRNA (log2 fold-change >0.4 and p-value <0.01false discovery rate [FDR] adjusted p-value < 0.05 by Benjamini-Hochberg method. R: replicate. B. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis of canonical pathways associated wih deregulated genes identified by RNAseq in A375 cells subjected to SPANX KD. C. Analysis using the Reactome database of cell cycle-related genes identified as downregulated by RNAseq in SPANX KD A375 cells. D. RT-qPCR confirmation of selected genes identified by RNAseq in A375 cells transduced with EV or SPANX-targeting shRNAs. E. Cell cycle analysis of A375 cells transduced with EV or SPANX-targeting shRNAs. F. Relative CDKN1A/p21 expression as determined by RNAseq in A375 cells transduced with EV or SPANX-targeting shRNAs. Statistical significance was assessed by Benjamini-Hochberg method, ***p-value < 0.001. G. RT-qPCR analysis of CDKN1A/p21 expression in A375 cells transduced with EV or SPANX-targeting shRNAs. H. RT-qPCR analysis of CDKN1A/p21 expression in A375 cells transduced with EV or an inducible vector encoding SPANXA grown in 3D, 3 days after doxycycline treatment (n=2). I. (left) β-galactosidase staining in A375 cells transduced with EV or SPANX-targeting shRNAs. Scale bars: 50μm. (right) Quantification of β-galactosidase-positive cells (n=5). Error bars represent means ± SEM. Statistical significance was assessed by one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s test, *p-value < 0.05, ***p-value < 0.001 in panels D, G and I.
