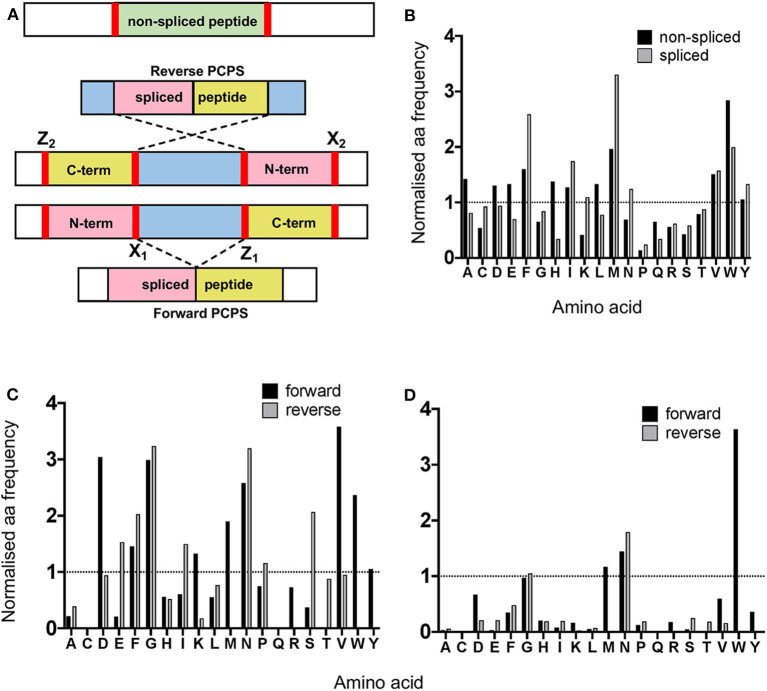
Figure 3.
Proteasomal cleavage preferences differ between canonical hydrolysis and PCPS reactions. (A) Schematic depicting cleavage sites employed to generate non-spliced and forward and reverse spliced peptides from precursor polypeptides. X1 and Z1 denote residues at cleavage sites acting as O-acyl enzyme intermediates and nucleophilic free amine groups (respectively) in forward PCPS reactions, while X2 and Z2 denote the corresponding residues in reverse PCPS reactions. (B) Comparison of global amino acid cleavage site usage for spliced and non-spliced peptides. Amino acid frequencies are normalized relative to the overall frequency of that amino acid within all 25 precursor polypeptides. (C) Normalized frequencies of amino acid residues acting as acyl-enzyme intermediates in forward and reverse PCPS reactions. (D) Normalized frequencies of amino acid residues acting as nucleophilic free amines in forward and reverse PCPS reactions. In (B–D), amino acids are defined using single letter code.