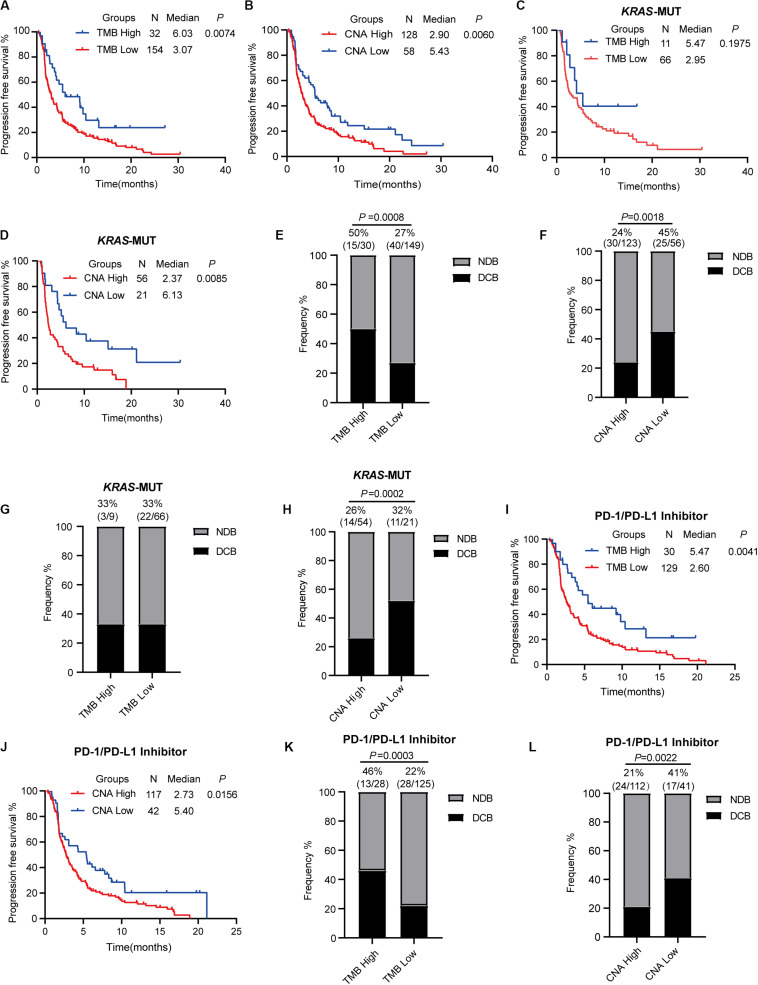
FIGURE 5.
Tumor mutation burden and copy number alteration burden correlated with clinical response to immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment. (A,B) Progression-free survival curve for patients receiving ICI (PD-1/L1 inhibitor or in combination with anti-CTLA-4) based on tumor mutation burden (A) or copy number alteration burden (B). (C,D) Progression-free survival curve for KRAS-mutant patients receiving ICI (PD-1/L1 inhibitor or in combination with anti-CTLA-4) based on tumor mutation burden (C) and copy number alteration burden (D). (E,F) Proportional representation of durable clinical benefits in advanced lung adenocarcinoma patients receiving ICI (PD-1/L1 inhibitor or in combination with anti-CTLA-4). (G,H) Proportional representation of durable clinical benefits in advanced KRAS-mutant lung adenocarcinoma patients receiving ICI (PD-1/L1 inhibitor or in combination with anti-CTLA-4). (I,J) Progression-free survival curve for patients receiving PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor alone based on tumor mutation burden (I) and copy number alteration burden (J). (K,L) Proportional representation of durable clinical benefits in advanced KRAS-mutant lung adenocarcinoma patients receiving PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor alone. MUT, mutant; WT, wild-type; DCB, durable clinical benefit; NDB, no durable clinical benefit.