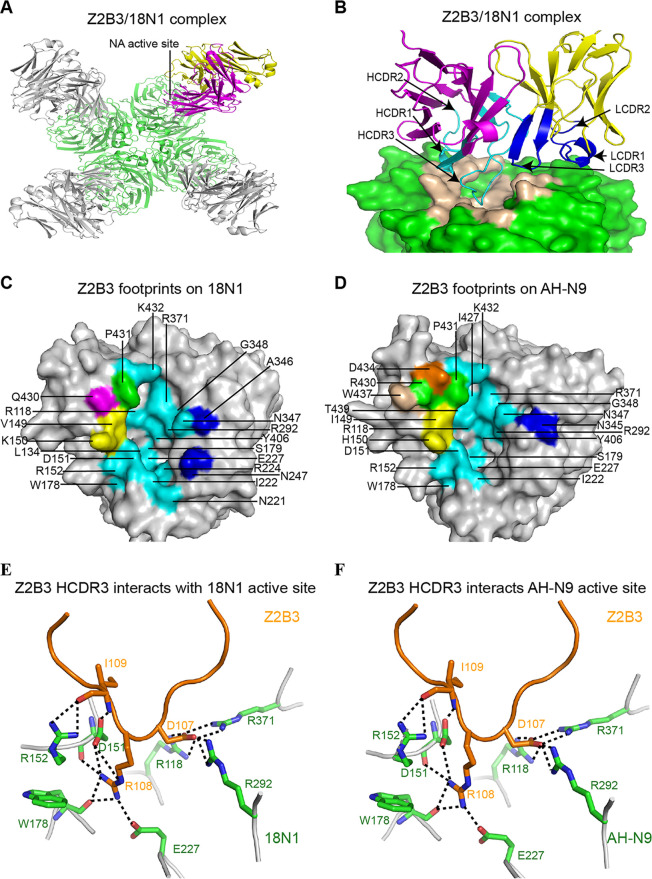
FIG 2.
Molecular determinants of Z2B3 with 18N1 and AH-N9. (A) Overall structure of Z2B3/18N1 complex, with NA in green and the heavy chain (HC) and light chain (LC) of one Fab in magenta and in yellow, respectively. Each NA monomer binds to one Z2B3 Fab. (B) The side view of the Z2B3/18N1 complex structure. The HC and LC of Z2B3 are colored in magenta and yellow, respectively. Residues of HC and LC involved in the interactions are colored in cyan and blue, respectively. The epitopes of Z2B3 are colored in wheat. (C and D) The footprints of Z2B3 on 18N1 (C) and AH-N9 (D). NAs are represented in the gray surface. Residues interacting with FR3, HCDR2, and HCDR3 are colored in wheat, magenta, and cyan, respectively. Residues that interact with both HCDR1 and HCDR2 are colored in orange. Residues that interact with both HCDR2 and HCDR3 are colored in yellow. Residues that interact with HCDR1, HCDR2, and HCDR3 are colored in green. Residues interacting with LCDR1 or LCDR3 are colored in blue. Residues contacted less than 4.5 Å are involved. (E and F) The interactions between residues in HCDR3 of Z2B3 and the key residues in the active site of 18N1 (E) or AH-N9 (F). The Z2B3 HCDR3 and NA are shown in orange and green, respectively, in the cartoon representation.