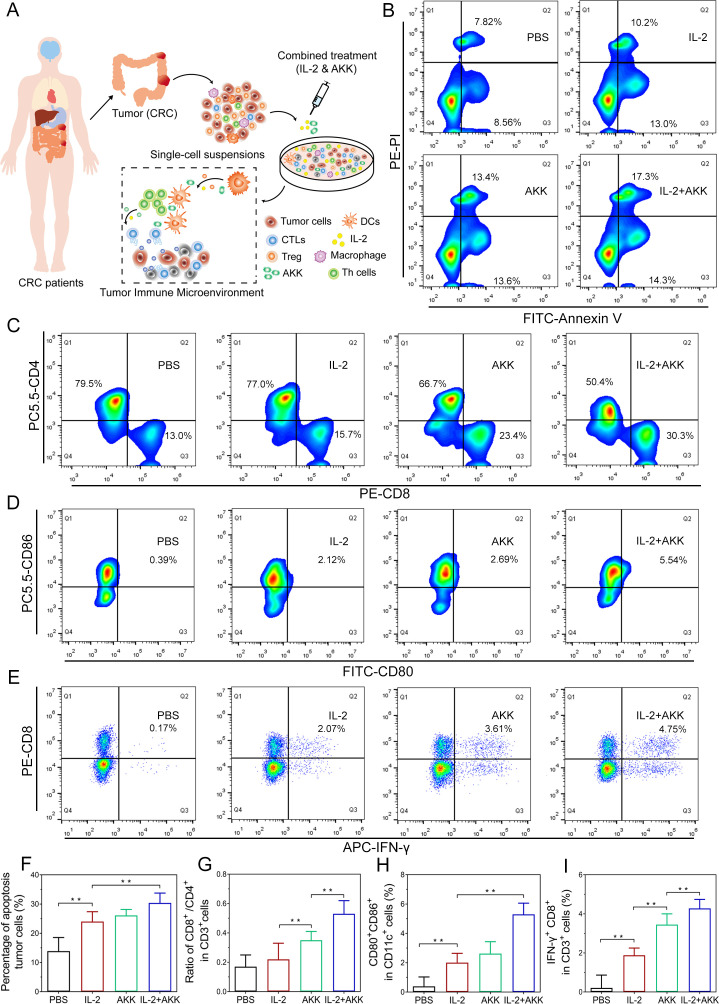
Figure 2.
Effects of combination treatment of IL-2 and AKK in ex vivo tumor tissues isolated from patients with CRC. Tumor tissues were dissociated into small pieces, digested and filtrated to generate single-cell suspensions. The cell suspensions were treated with AKK and IL-2 in combination or individually. (A) Schematic illustration of combination treatment of IL-2 and AKK in CRC patient-derived ex vivo tumor tissues. (B) Tumor cells were collected and stained with FITC-conjugated Annexin-V and PI for apoptosis detection by flow cytometry. (C–E) Representative flow cytometry analysis of CD8+/CD4+ ratio in CD3+ T cells (C), activated DCs (D) and cytotoxic effector T cells (E) in tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes isolated from patients with CRC. (F–I) Percentage of apoptosis tumor cells among different groups (F), ratio of CD8+/CD4+ in CD3+ T cells (G), CD80+ CD86+ in CD11c+ cells (H) and IFN-γ+ CD8+ in CD3+ T cells (I). All data are shown as mean±SD (n=3) (**p<0.01). AKK, Akkermansia muciniphila; APC, allophycocyanin; CRC, colorectal cancer; CTL, cytotoxic T lymphocyte; DC, dendritic cell; FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; IFN, interferon; IL-2, interleukin-2; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; PE-PI, phycoerythrin-propidium iodide.