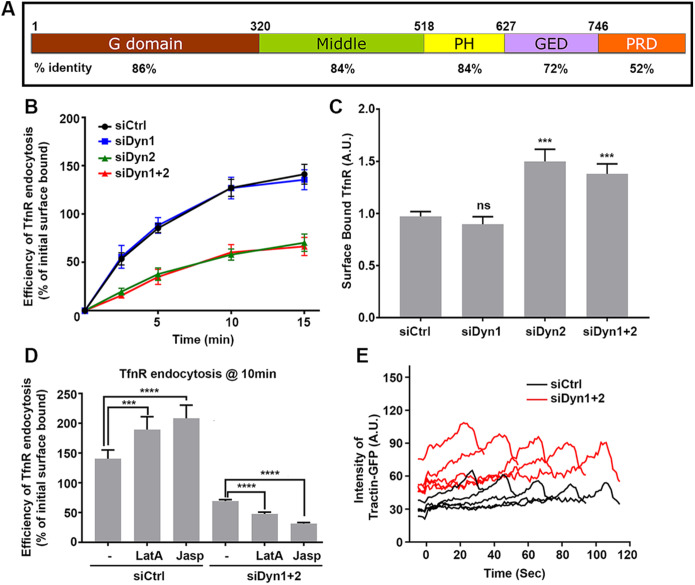
FIGURE 1:
Differential functions of dynamin isoforms in CME of nonneuronal cells. (A) A schematic representation of the domain structure and sequence identity of dynamin isoforms. (B) Effect of KD of dynamin isoforms on the efficiency of TfnR endocytosis in ARPE cells. The cells were treated with siRNAs as indicated and the efficiency of TfnR endocytosis was measured by in-cell ELISA assay and presented as the percentage of initial surface-bound TfnR. Data shown are average ± SD. (C) Quantification of surface accumulation of TfnR after KD of Dyn1, Dyn2, and Dyn1+2, as indicated (n = 3 independent biological repeats). (D) Effect on TfnR uptake efficiency in control and Dyn1+2 double KD cells with/without 30 min preincubation with chemicals affecting actin polymerization/depolymerization dynamics: latrunculin A (latA, 100 nM) and Jasp (1 µM). Statistical significance was calculated by t test. In this and subsequent figures, *p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01; ***p ≤ 0.001; ****p ≤ 0.0001; n = 3 independent biological repeats. (E) ARPE cells expressing mRuby-CLCa and Tractin-eGFP were plated on gelatin-coated coverslips and imaged by TIRFM. Shown are the intensity profiles of the recruitment of Tractin-eGFP (secondary channel) to the indicated lifetime cohorts of mRuby-CLCa containing CCPs (primary channel). The TIRFM data are representative of two independent biological repeats.