Figure 2.
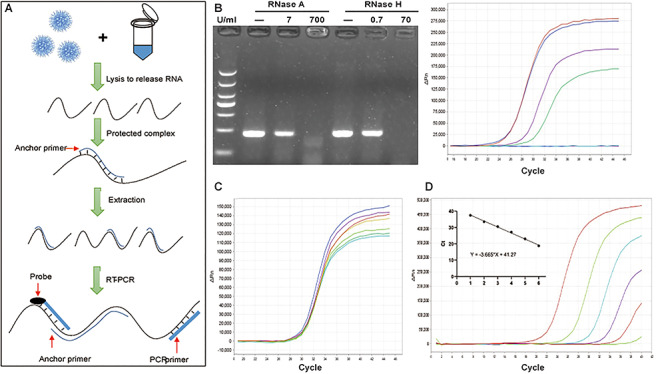
The detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA by AP-PCR in sputum spiked with SARS-CoV-2 RNA. A. Schematic illustration of the AP-PCR procedure. Mixing the sputum specimens (spiked with SARS-CoV-2RNA) with lysis buffer containing AP led to the formation of DNA:RNA hetero-complexes. This was followed by RT-PCR amplification of 215 bp fragment of the N gene of SARS-CoV-2 RNA. B. In the sputum from healthy volunteers spiked with SARS-CoV-2 RNA, AP improved RT-PCR amplification after the RNase R treatment. C. In sputum spiked with SARS-CoV-2 RNA, we determined the effect of varying concentrations of AP (with fixed PCR primers) and varying PCR primers (with the fixed AP) on AP-PCR amplification efficiency. Varying concentrations of AP or PCR primers did not affect AP-PCR amplification efficiency (P = 0.52). D. The determination of the LOD of the AP-PCR assay using sputum spiked with series of 10-folddilution of SARS-CoV-2 RNA (20-2095 copies/ml). The negative linear correlation was established with β as -3.665 (r = 0.995, P < 0.0001).
