Figure 4.
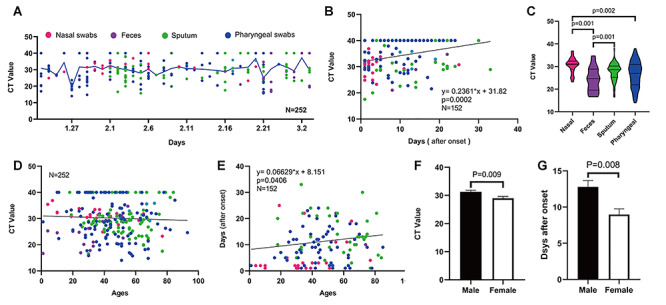
Prolonged SARS-CoV-2 RNA loading and its associated factors of age and sex as revealed by the AP-PCR. A. The chronological changes of SARS-CoV-2 RNA loading during epidemics in Zhejiang province from 23 January to 3 March 2020. The viral RNA loading from different collecting sites was evenly distributed throughout the epidemic period (color symbol = specimen type). B. There was a positive linear correlation between the days after the first positive diagnosis and the CT Value (r = 0.091, P = 0.0002). C. The biodistribution of SARS-CoV-2 RNA loading among four different collecting sites: Analysis of the 252 confirmed patients showed the highest positive rates in Nasal swabs (96%), followed by sputum (76.7%), pharyngeal swabs (74.6%), feces (69.6%). D. There was no correlation between the CT value and age (r = 0.0021, P = 0.463). E. Older age was associated with a longer duration of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA loading (r = 0.002159, P = 0.0406). F. Male patients have lower SARS-CoV-2 RNA loadings than female, as evidenced by higher Ct value in male (n = 132, 31.3 ± 0.57, mean ±SE) than female (n = 120, 29±0.66 mean ± SE) in specimens from 252 confirmed cases (P = 0.0086, t-test). G, Male COVID-19 patients showed the longer duration of the viral RNA loading by 4 days when compared to female patients after the first positive test (P = 0.0077, t-test).
