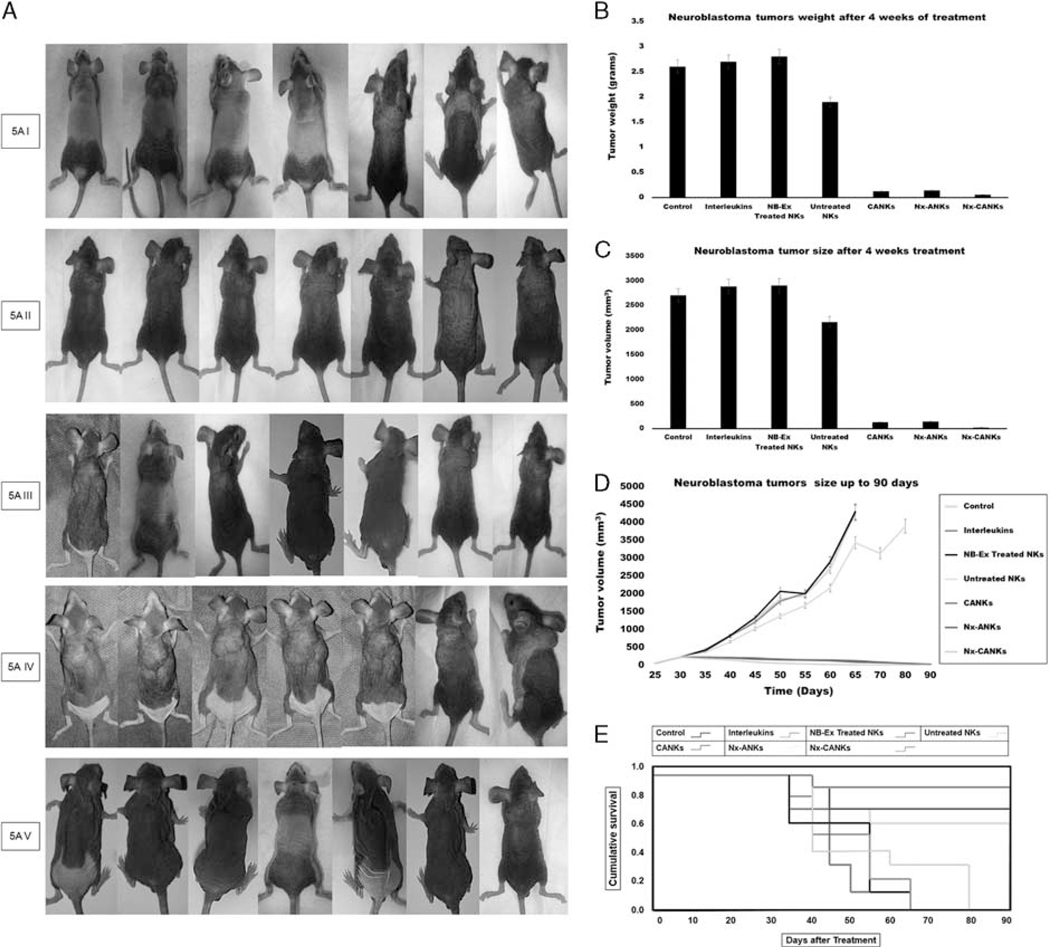
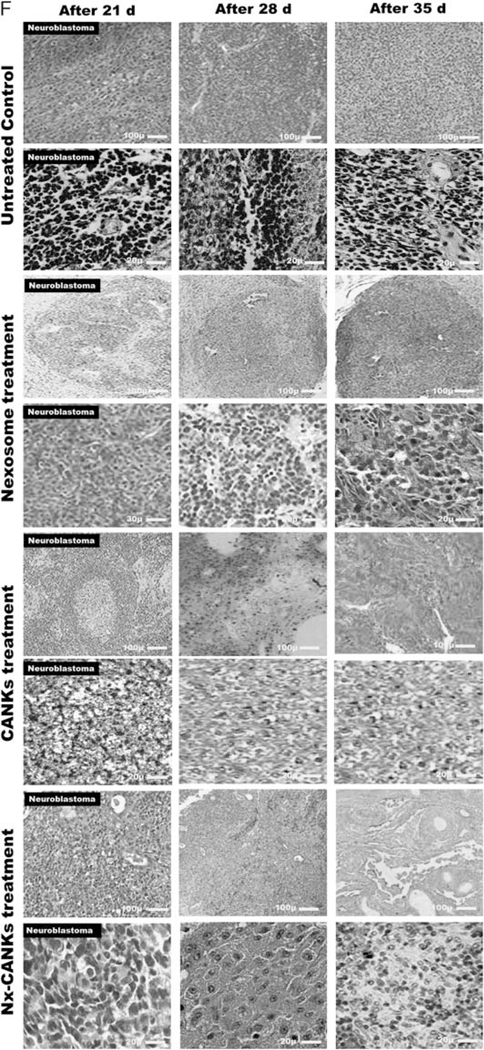
FIGURE 6.
A, Tumor formation in different groups of mice. Neuroblastoma tumor growth in nude mice is obvious after 4 weeks. The row I shows tumor formation in mice that did not receive any other treatment and served as tumor control group. Row II shows the fresh NK effect on the mice bearing NB cells after 28 days of injection. Row III shows the nexosome-treated NK effect on mice bearing NB cells after 28 days of injection. Row IV shows NB-Ex-treated NK effect on mice bearing NB cells, and row V shows the Nx-CANKs-treated mice after 28 days of injection. B, NB tumor weights after 4 weeks of treatment. The diagram shows a −3 g NB tumor in mice treated with NB-Exosomes. The fresh NK can reduce the tumor weight, but nexosome-treated NKs have a similar effect to that of cytokine-activated NKs to reduce tumor weight under 0.2 g (P < 0.05). C, NB tumor volumes after treatments. The best effect of treatment on tumor volumes after 4 weeks was achieved by Nx-CANKs that destroyed 86% of tumors completely. D, NB tumor sizes after 90 days of treatment. The nude mice were checked every 3 days and killed on day 95. The tumor volumes in CANKs, Nx-ANKs, and Nx-CANKs were drastically smaller than that of other groups in order (*P < 0.05). E, Kaplan-Meier Graph. There is a significant difference in survival of 7 different groups of NB tumor–bearing mice of up to 90 days. An overall 86% survival for Nx-CANKs and no survival for NB-Ex-treated groups (*P < 0.05). F, Histology. Hematoxylin-eosin staining of resected NB tumors after 3, 4, and 5, weeks of treatment shows that we had a minimum of neoplastic cells after 5 weeks’ treatment with Nx-CANKs as our best complementary treatment group. NB indicates neuroblastoma; NB-Ex, NB-derived exsosomes; NK cell, natural killer cells; Nx-ANKs, NB exosome–activated NK; Nx-CANKs, NB exosome cytokine-activated NKs.