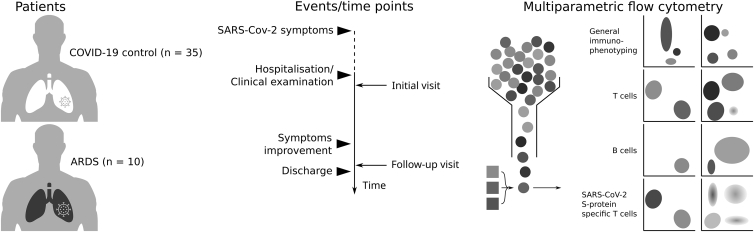
Figure 1.
Study Outline
45 patients consecutively admitted to Marienhospital Herne–Universitätsklinikum der Ruhr-Universität Bochum (North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany) and Universitätsklinikum Essen (North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany) were enrolled in this study. The patients were classified based on their symptoms as non-critical COVID-19 course (COVID-19 control) or COVID-19-associated ARDS (ARDS). The patients were analyzed at two time points: shortly after hospitalization (initial visit) and after clinical improvement (follow-up visit). For the ARDS group, the initial visit corresponds to the first available visit after ARDS symptoms were observed, and the follow-up visit corresponds to discharge from the intensive care unit (ICU). The profiling included evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 S-protein-specific IgG serum antibodies, as well as phenotyping of all major immune cell populations by flow cytometry, and characterization of B and T cell subsets. T cells reactive to the SARS-CoV-2 S-protein were also analyzed by application of overlapping peptide pools.