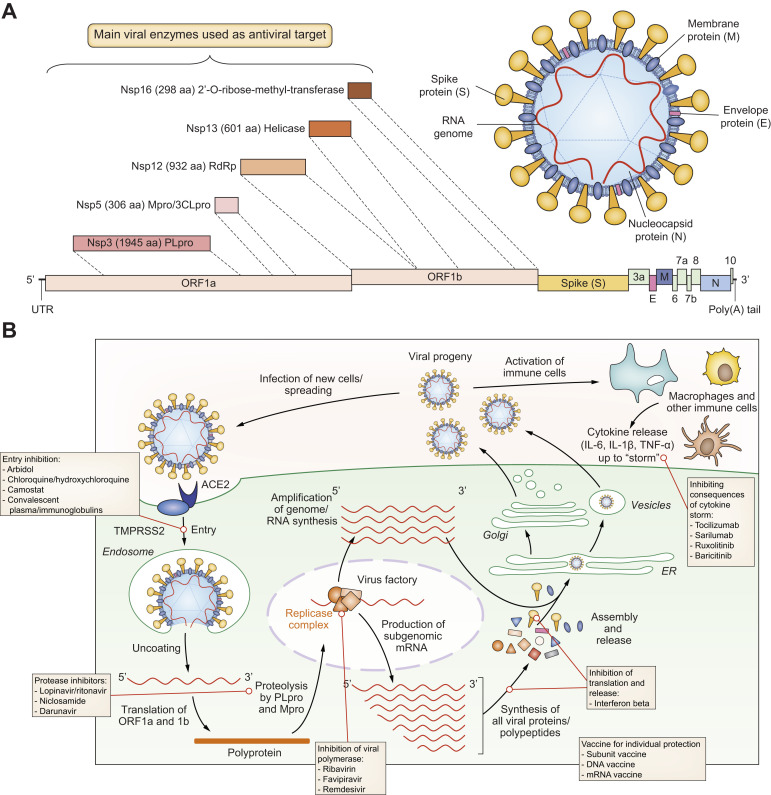
Fig. 1.
Virology, replication cycle and targets for drug development.
(A) Coronaviruses have a long, capped and poly-adenylated RNA genome, which contains between 8 to 10 ORFs, allowing structural, non-structural and accessory viral protein synthesis.87 SARS-CoV-2 is 29,903 base-long and contains 6 majors ORFs, as well as additional accessory genes; the reference sequence is registered in GenBank with ID: MN908947.3.1 (A, B) Up to 28 different polypeptides are potentially produced in fine from the different ORFs and after polyprotein processing by viro-encoded proteases.87 If the RNA genome contained in virions can already serve, after cell entry, as a template for the synthesis of non-structural proteins, which are involved in the early phase of virus replication (mainly by forming the replicase complex), subgenomic messenger RNAs are also produced in the late phase of the cycle to allow the synthesis of structural proteins (e.g. spike (S), envelope (E), membrane (M) and nucleocapsid (N) proteins), as well as other accessory polypeptides. Another main replication intermediate is the complementary minus-sens RNA, which is used by the viro-encoded RdRp, within the replicase complex, to amplify the full-length genome, which is then capped and polyadenylated by both viral and host enzymes before being incorporated into the viral progeny. (B) After entry into ACE2-positive (entry receptor) and TMPRSS2-positive (co-factor for entry) cells, and membrane fusion (i.e. uncoating process), a full-length genome is released into the cytoplasm of cells. This full-length polycistronic RNA is directly used to efficiently encode a polyprotein from the first ORFs present on the molecule, starting from 5′ extremity, i.e. ORF1a and ORF1b; the latter is read after a frame-shift from ribosomal scanning of ORF1a. (A, B) The polyprotein is then processed by 2 viro-encoded proteases, PLpro/Nsp3 and 3CLpro/Nsp5 (also known as main protease [Mpro]), into 16 proteins/polypeptides (Nsp1 to 16). (B) These non-structural proteins/polypeptides are important for the early stages of infection, as they enable the formation of the replicase complex around the RdRp enzymatic activity, which is involved in the synthesis of negative-sense full-length RNA, as well as subgenomic messenger RNAs by a discontinuous transcription strategy.87 The latter enables the efficient and stochiometric synthesis of all other viral proteins/polypeptides, which are important for virus assembly and release of progeny virions. (B) Specific targets for drug development and current treatment options are indicated. ACE2, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; 3CLpro/Nsp5, chemotrypsin-like protease; ORF, open reading frame; PLpro/Nsp3, papain-like cysteine protease; RdRp, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus 2.