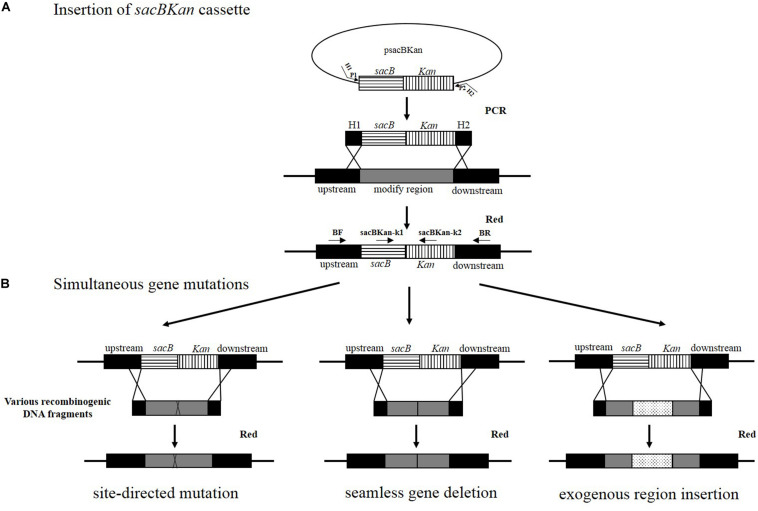
FIGURE 1.
Rationale of the simultaneous gene multiple modifications approach. (A) In the first step, the sacBKan cassette obtained by using primers H1P1/H2P2 is inserted into the target locus using the red homologous recombination system, and Kan-resistant strains are selected. H1P1/H2P2 included 40- to 50 nt extensions (H1/H2) homologous to regions adjacent to the target-specific locus and 20 bp sequences corresponding to the P1/P2 sequences from psacBKan. Proper sacBKan cassette insertion mutant is confirmed by using locus-specific primers (BF and BR) with the corresponding common test primer (psacBKan-k1 or k2) dependent on four reactions by using primer pairs BF/BR, BF/psacBKan-k2, psacBKan-k1/BR, and psacBKan-k1 or k2. (B) In the second step, different types of DNA recombinogenic DNA fragments with short homologous arms obtained by using seamless assembly technology are introduced by electroporation to construct site-directed mutation, seamless gene deletion, and exogenous region insertion. Finally, the sucrose-resistant clones are selected on LB plates with 8% sucrose. Positive clones are confirmed by using primer locus-specific primer BF/BR and sequencing.