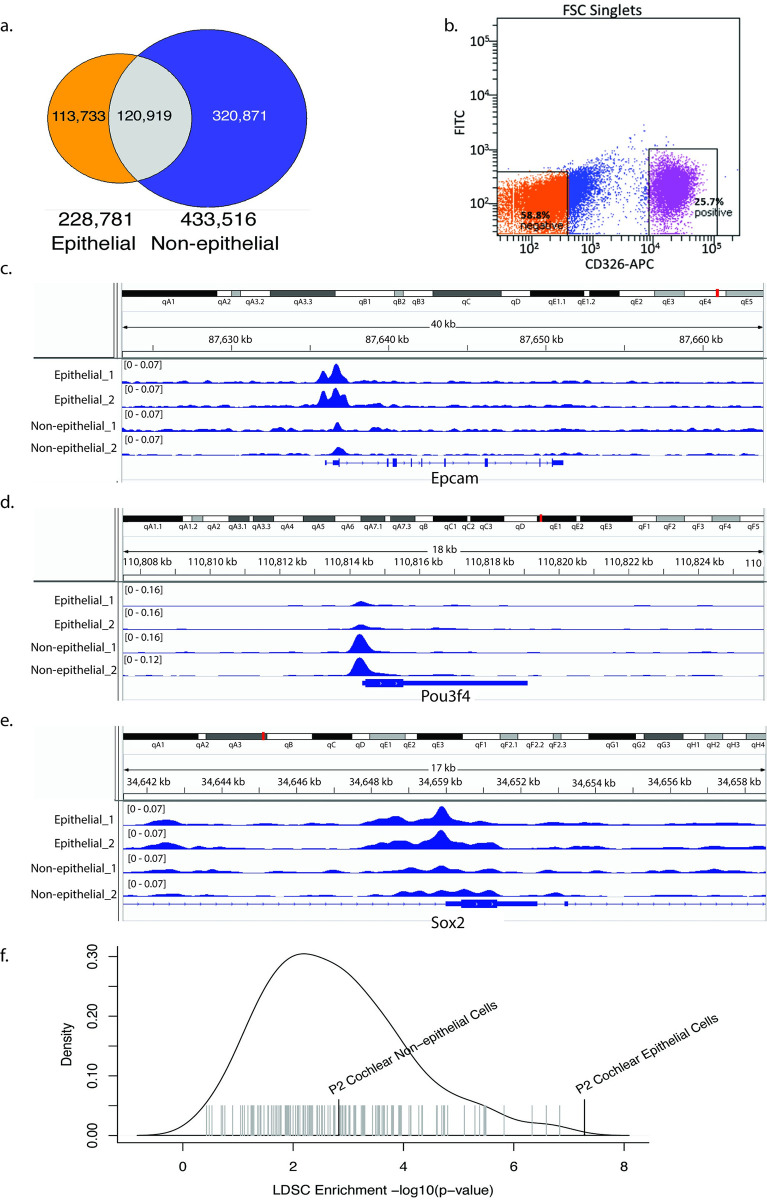
Fig 3. Heritable risk for hearing difficulty is enriched at open chromatin regions in cochlear epithelial cells.
a. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) of cochlear cells. Cochlear cells were labeled with a CD326 antibody conjugated to Allophycocyanin (APC), and sorted two ways as CD326 (+) and CD326 (-). b. Overlap of open chromatin regions identified by ATAC-seq of epithelial vs. non-epithelial cells in the mouse cochlea. c-e. Open chromatin peaks near cell type-specific marker genes: Epcam (b), Pou3f4 (b), and Sox2 (c). f. -log10(p-value) for enrichment of hearing difficulty risk in regions of the human genome homologous to open chromatin in epithelial and non-epithelial cells from mouse cochlea (black vertical lines) and in non-cochlear cell types from ENCODE (gray lines) https://umgear.org/p?l=3a70e6e7.