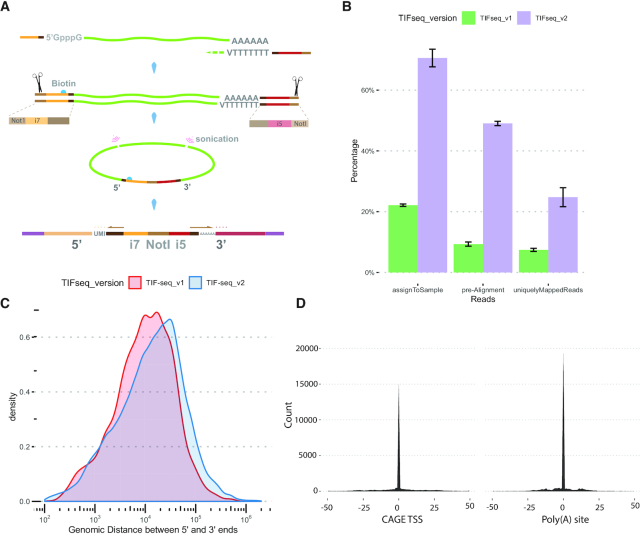
Figure 1.
Genome-wide measurement of transcript isoforms with TIF-Seq2. (A) Capped and polyadenylated RNA used as template to generate full-length cDNA, which then circularized and fragmented using sonication. Streptavidin magnetic beads were used to purify the fragments spanning the 5′ and 3′ end of cDNA and then were used for Illumina library preparation. The arrows indicate the direction of sequencing reads extension (more details in Supplementary Figure S1). (B) Informative reads fetched from TIF-Seq1 (n = 3) and TIF-Seq2 (n = 4). TIF-Seq2 can fetch more useful reads that are assigned to samples, reads passed quality control for alignment and the uniquely mapped reads. (C) Genomic distance between 5′ and 3′ ends captured by TIF-Seq1 and TIF-Seq2. The enzymatic optimization of TIF-Seq2 can improve the lengths of RNA molecules (average distance: 20 kb in TIF-Seq1 and 35 kb in TIF-Seq2). (D) Transcript boundaries agree with the transcription start sites (TSSs) defined by CAGE (12) and the poly(A) sites defined by 3′ sequencing (13).