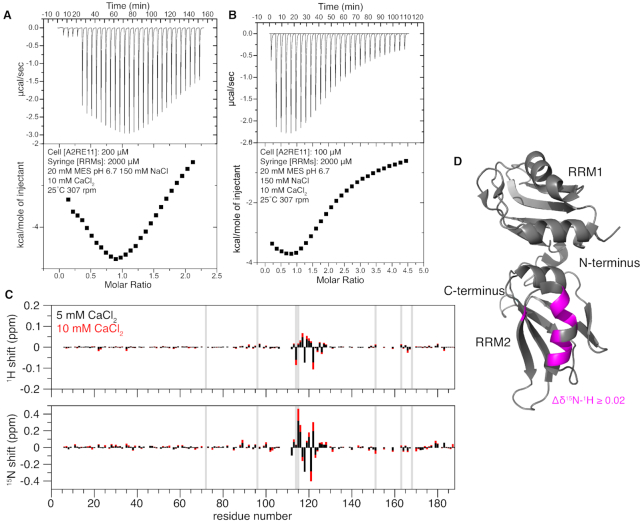
Figure 3.
hnRNPA2 RRM2 binds calcium ions. (A) ITC of the RRMs binding to rA2RE11 in the presence of calcium. The isotherm has a biphasic curve consistent with multiple binding, indicating that the presence of calcium is altering the binding of the RRMs to the RNA, although the apparent binding affinity does not increase. (Note that the small peaks in the beginning of the thermogram were caused by a series of 5 small (2 μl) injections to ensure reliable data for the first large injection used for isotherm quantification). (B) ITC of the RRMs binding to rA2RE11 in the presence of calcium at half the concentration of RNA. The isotherm still has a biphasic curve consistent with multiple binding events, indicating that the presence of calcium is altering the binding of the RRMs to the RNA. (C) Chemical shift deviation of hnRNPA2 RRMs with 5 or 10 mM CaCl2 added. Chemical shift deviations indicate the presence of a binding pocket for calcium in the second RRM around residues 110–125. Vertical grey bars indicate histidine residues, showing that the shifts are not localized to histidine positions and therefore unlikely to be due to possible slight deviations in pH. (D) Average CSPs for the 10 mM CaCl2 condition plotted onto 5HO4 suggest that Ca2+ primarily binds a single helix at the back of RRM2.