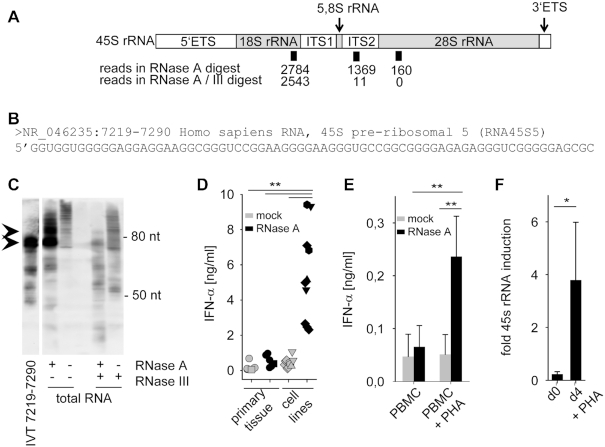
Figure 2.
Identification of an ITS2-derived immunostimulatory RNA fragment. (A) Schematic illustration of 45S rRNA, consisting of 5.8S, 18S and 28S as well as internal and external transcribed spacers (ETS, ITS). Positions and number of sequence reads in RNase A and RNase A / RNase III digested and size-fractionated samples A' and A'' (see Figure 1C) are depicted. (B) Sequence of most common read specifically found in the RNase A-digested but not in the RNase A / RNase III-digested sample. (C) Northern blot analysis of undigested, RNase A, RNase III or RNase A/RNase III digested HEK293 RNA with a specific probe for 45S rRNA 7219–7290. IVT-transcribed fragment 7219–7290 served as positive control. (D) Human PBMCs were stimulated for 20 h with 2 μg/ml mock-treated (grey symbols) or RNase A-digested RNA (black symbols) from primary tissue such as human PBMCs (five samples, circle), murine liver (one sample, square) or tumor cell lines such as HeLa (one sample, triangle up), Vero (two samples, hexagonal), MDCK (two samples, triangle down) and HEK293 (five samples, diamond). IFN-α was measured by ELISA. *** P < 0.001. (E) Human PBMCs and monocytes were stimulated with 2 μg/ml mock-treated (grey bars) or RNase A-digested RNA (black bars) from PBMCs, or with RNA from PBMCs activated with PHA for 4 days. IFN-α was measured by ELISA. Graph combines three independent experiments each in biological duplicates (six measurements per data point ± S.D.), ** P < 0.01. (F) 45S rRNA levels of unstimulated or PHA stimulated PBMCs were determined by RT-PCR targeting the 5.8S/ITS2 region. Three combined independent experiments are shown each in biological duplicates (six measurements per data point ± S.D.), * P < 0.05.