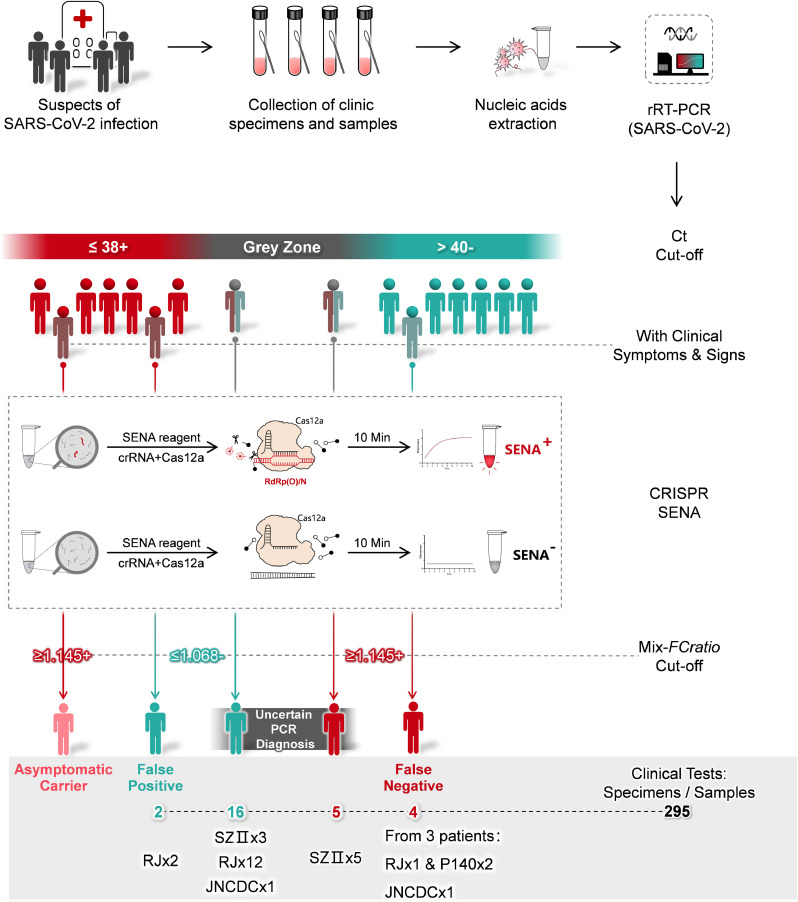
Fig. 1.
Schematic description of SENA and its application as a confirmation diagnosis for rRT-PCR diagnosis of COVID-19. Generally, nucleic acids are extracted from the clinical specimens such as pharyngeal swabs of the suspects of SARS-CoV-2 infection and then subject to rRT-PCR analysis. The diagnostic reports are based on the Ct cut-off values guided by the supplier of rRT-PCR kits. However, high Ct-value designated “grey zone” associated uncertain fuzzy readouts are often encountered. Besides, some probably false-positive or false-negative cases may be indicated by their atypical clinical symptoms or signs. For all these cases, the corresponding rRT-PCR products can be sent to another physically isolated room for SENA analysis and the ambiguity may be clarified by SENA with its positive and negative cut-off mix-FCratio. The real-life data related to these scenarios revealed in this study are shown in the figure and details are illustrated in the text. RJ, JNCDC and SZII are the names of the hospitals and the number indicates the overall number of patients identified. While P140 was a patient in DF hospital, and two distinct samples from P140 were identified to be false-negative. For details, please ref to Supplementary Table 3.