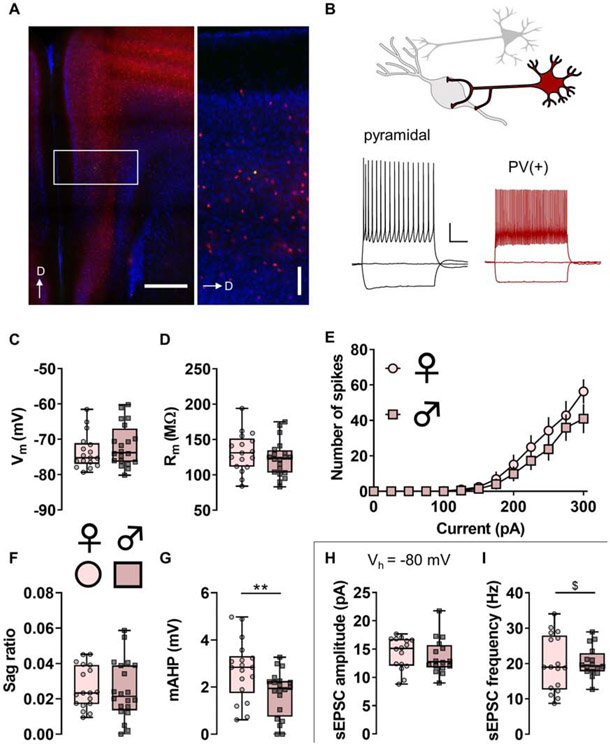
Figure 2. Parvalbumin (PV)-(+) neurons display functional characteristics of fast-spiking interneurons.
(A) Left, Representative image displaying TdTomato fluorescence (red) in PV-expressing neurons in the mouse prefrontal cortex (PFC). Right, boxed inset showing PV-IN distribution throughout layers of prelimbic PFC. PV-INs are highly expressed within layer 5 and rarely present within layer 1 of the mouse PFC. A representative PV-IN was infused with Alexa 488 dye (green). Scale bars indicate 500 μm and 100 μm. D, dorsal. (B) Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings were made from identified neurons in the PFC. Representative current-clamp recordings from an unlabeled pyramidal cell (left, black) and a TdTomato-labeled PV-IN (right, red). The pyramidal cell displays a hyperpolarization-activated sag and accommodating spike firing, physiological features that are minimal or absent in PV-INs. Scale bars indicate 20 mV and 250 ms. (C) Resting membrane potential (Vm) in PV-INs from female mice (circles) and male mice (squares). n/N = 17/9, 20/8 cells/mice per group. (D) No difference in membrane resistance (Rm) between PV-INs from female and male mice. n/N = 17/9, 20/8. (E) No difference in current-evoked spiking between PV-INs from female and male mice. n/N = 16/9, 18/8. (F) No difference in hyperpolarization sag ratio between PV-INs from female and male mice. n/N = 18/9, 20/8. (G) PV-INs from female mice display greater medium afterhyperpolarization (mAHP) than PV-INs from male mice (2.71 ± 0.30 vs 1.72 ± 0.22 mV, **: p < 0.01, Mann-Whitney U test). n/N = 18/9, 20/8. (H) After current-clamp recordings, cells were switch to voltage-clamp configuration and held at −80 mV, the reversal potential for chloride. No difference in spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic current (sEPSC) amplitude between PV-INs from female and male mice. n/N = 16/9, 16/7. (I) No difference in the mean of sEPSC frequency between PV-INs from female and male mice. A difference in the variance of sEPSC frequency was observed between female and male mice (F16,15 = 3.526, $: p < 0.01, F test to compare variances). n/N = 17/9, 16/7.