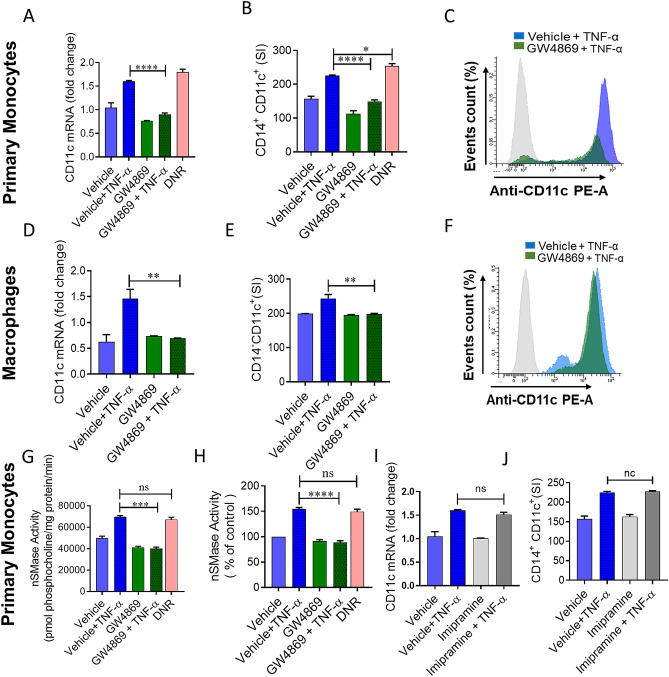
Figure 1.
nSMase inhibition blocks TNF-α mediated pro-inflammatory changes in human monocytes/macrophages. Primary monocytes were pretreated with nSMase inhibitor (GW4869: 10 µM), nSMase agonist (DNR; 1 µM) or vehicle for 1 h and then incubated with TNF-α for 2 h. Cells were harvested, and mRNA of CD11c was determined by real time RT-PCR (A). After 6 h treatment with TNF-α, cells were stained with antibodies against CD14 and CD11c along with matched isotype controls. Surface expression of CD14+CD11c+ was assessed by flow cytometry, (B) data are presented as a bar graph of mean staining index, and (C) representative histogram. Macrophages derived from monocytes were pre-incubated with (GW4869: 10 µM) for 1 h and then treated with TNF-α. (D) CD11c mRNA expression and (E,F) surface expression of CD14+CD11c+ were assessed by flow cytometry. Monocytic cells (Primary monocytes) were pretreated with nSMase inhibitor (GW4869: 10 µM) or vehicle for 1 h and then incubated with TNF-α for 10 min. (G) nSMase activity measured in in equal amount of protein (20 µg); (H) nSMase activity as percentage of expression to vehicle. Primary monocytes were pretreated with aSMase inhibitor (lim: 10 µM) or vehicle for 1 h and then incubated with TNF-α for 2 h or 6 h. (I and J) Cells were harvested, and mRNA of CD11c and surface expression of CD14+CD11c+ cells were determined. Unstimulated cells were used as controls for different treatments. The results obtained from minimum three independent experiments with three replicates of each experiment are shown. All data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n ≥ 3). *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001 versus vehicle.