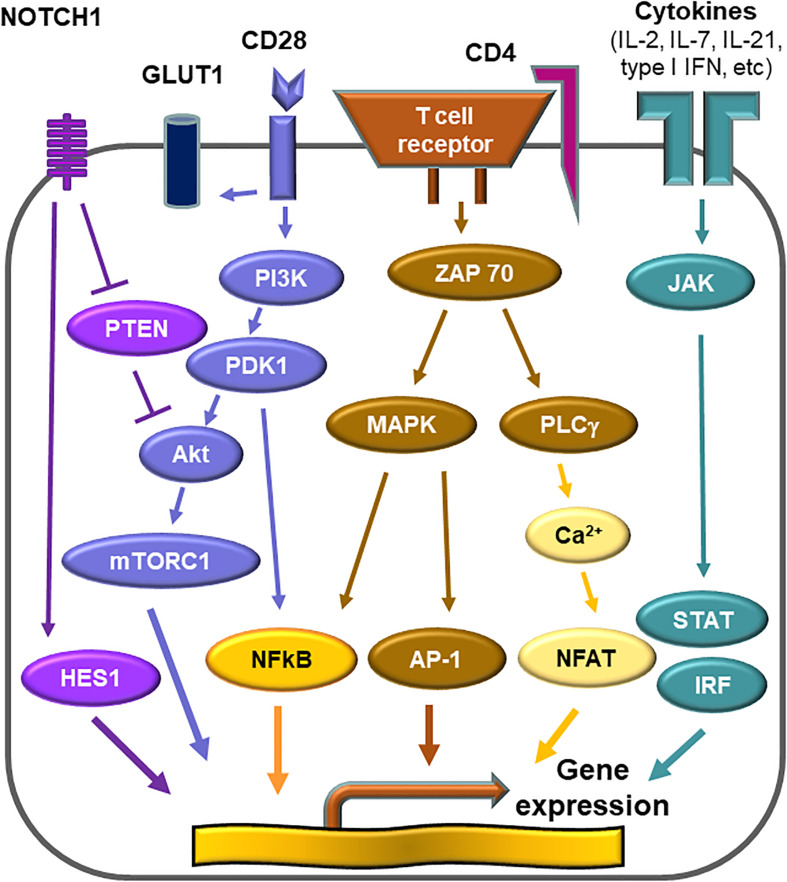
FIGURE 6.
Druggable signaling cascades in vasculitogenic T cells. Numerous signals converge to shape the activation patterns of T cells. In the case of vasculitis-inducing T cells, vasculitogenic antigens trigger the T cell receptor activation cascade. Several co-stimulatory signals adjust signal strength and duration and thus determine differentiation, effector functions and longevity of the T cell. CD28-dependent signaling regulates the metabolic program of vasculitogenic T cells. CD28-mediated signals activate mTORC1, thus determining T cell proliferation and lineage assignment. Persistent NOTCH signaling is a signature abnormality of vasculitogenic CD4+ T cells and regulates tissue invasiveness. Cytokines modulating T cell function utilize the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Disease-relevant cytokine signals derive from IL-2, IL-7, and, possibly, from type 1 interferon.