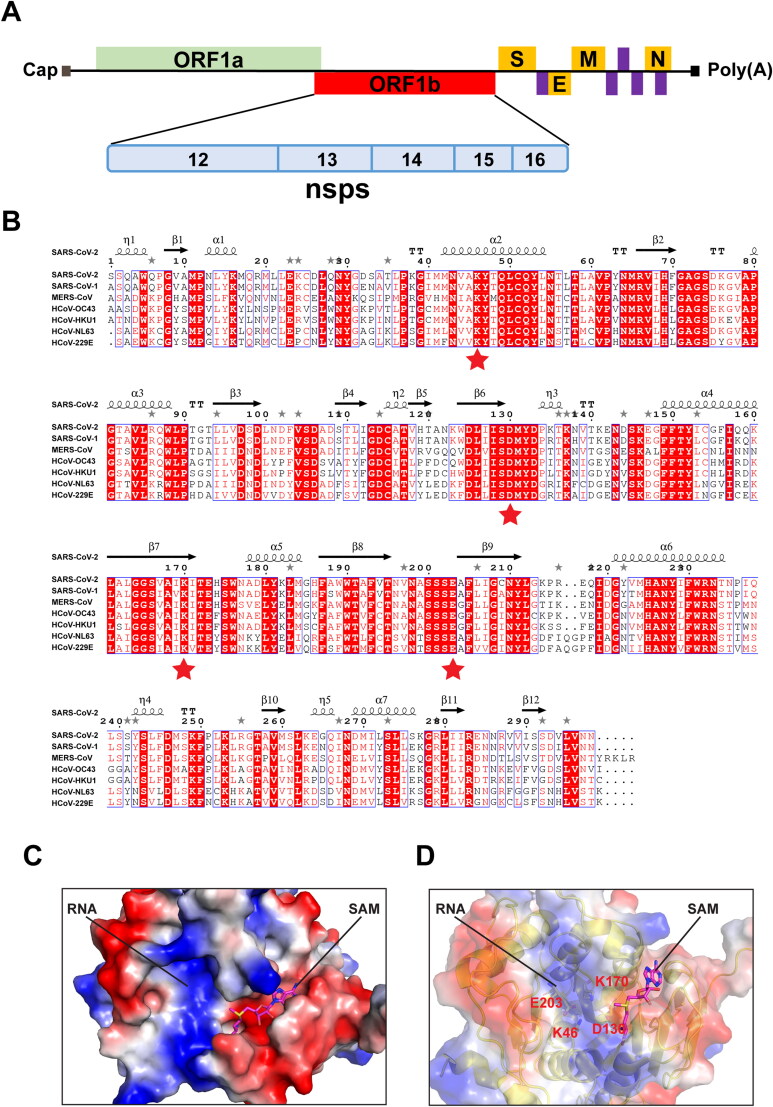
Figure 1.
Comparative analysis of primary amino acid sequences and crystal structures of CoV 2’-O-MTases. (A) Schematic presentation of the SARS-CoV-2 genome organization. Expression of two open reading frames (ORF1a and ORF1b) yields 16 nsps, including 2’-O-MTase nsp16. S, E, M, and N indicate the four structural proteins: spike, envelope, membrane, and nucleocapsid. (B) Sequence alignment of nsp16 proteins derived from genome sequences of the following: SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV-1, MERS-CoV, HCoV-OC43, HCoV-HKU1, HCoV-NL63, and HCoV-229E. The secondary structure of SARS-CoV-2 nsp16 is shown above. Residues with 100% conservation are indicated in solid red boxes and those with identity of 70% or higher are depicted in light red color. The red stars indicate the conserved KDKE motif in 2’-O-MTases. (C) Surface representation of the SAM binding pocket and the RNA binding groove in SARS-CoV-2 nsp16 with coloring according to the electrostatic potential. The surface electrostatic potential diagram (±5 kT/e) in SARS-CoV-2 nsp16 (PDB: 6W4H Chain A) was generated by PyMol; the blue areas represent positively charged areas, while the red areas represent negatively charged areas. (D) The KDKE catalytic tetrad motif is located at the bottom of the RNA binding groove of nsp16.