FIGURE 1.
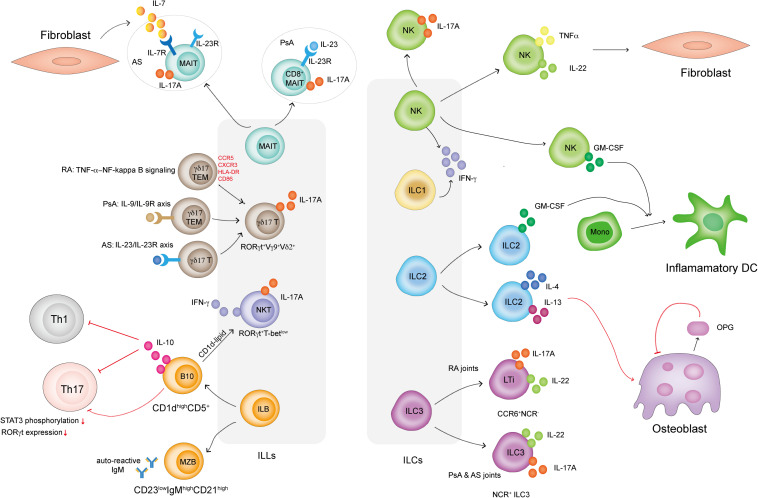
How ILLs and ILCs are involved in IA. MAIT cells in PsA patients display a CD8+IL-23R+ phenotype and respond to IL-23 to produce IL-17A. MAIT cells in AS patients display an IL-7R+IL-23R+ phenotype but only respond to FLS-derived IL-7 to produce IL-17A. γδ17 T cells in IA are RORγt+Vγ9+Vδ2+. γδ17 T cells in RA display the TEM phenotype and highly express CCR5, CXCR3, HLA-DR, and CD86. TNFα activates NF-κB signaling in γδ17 T cells and promotes IL-17A secretion. γδ17 T cells are activated via the IL-9/IL-9R and IL-23R/IL-23R axes in PsA and AS patients, respectively. NKT cells in IA are RORγt+T-betlow and preferentially secrete IL-17A. ILB cells include CD23lowCD21high MZB cells, which secrete autoreactive IgM in IA, and CD1dhighCD5+ B cells, which produce IL-10 to dampen Th1 and Th17 cell responses. B10 cells also directly inhibit Th17 cell responses by reducing STAT3 phosphorylation and RORγt expression. B10 cells present CD1d-lipids and induce iNKT cells to secrete IFN-γ. IL-17-producing NK cells are present in the SF in IA. NK cells also produce TNF-α and IL-22, which induce FLS proliferation. Both NK cells and ILC2s in IA secrete GM-CSF, which induces a proportion of monocytes to differentiate into inflammatory DCs. ILC2s in IA also produce IL-4 and IL-13, well-known Th2-related cytokines that induce osteoblasts to produce OPG. OPG is an inhibitor that prevents osteoclast formation. ILC3s can be classified into CCR6+NCR– LTi cells and NCR+ ILC3 cells. Both subsets secrete IL-17A and IL-22. LTi cells mainly exist in RA joints, while NCR+ ILC3 cells can be found in the joints of PsA and AS patients.