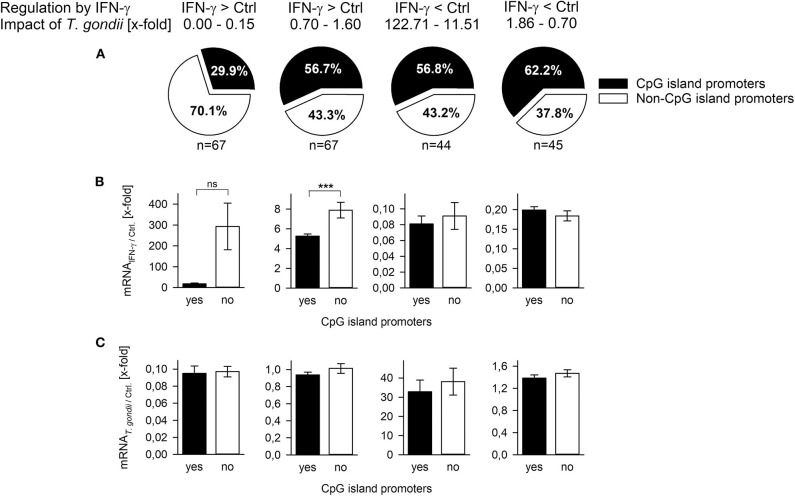
Figure 2.
T. gondii preferentially inhibits expression of IFN-γ-induced genes regulated by non-CpG island promoters. Genes (n = 223) were selected from a previous microarray analysis (20), and they were grouped according to their regulation by IFN-γ (up- or down-regulated) and the x-fold regulation by concomitant infection with T. gondii. (A) They were in silico analyzed for presence or absence of CpG islands within nucleotides −200 to +200 relative to the transcriptional start site. Fold mRNA regulation induced by IFN-γ in non-infected cells (B) or by T. gondii compared to non-infected controls (C) were calculated for genes with or without CpG island promoters. Bars represent means ± S.E.M.; differences between groups were evaluated by Student's t-test (***p < 0.001; ns, not significant).