Figure 2.
In Vitro Characterization of Traceable pan-ErbB Family CAR T Cells
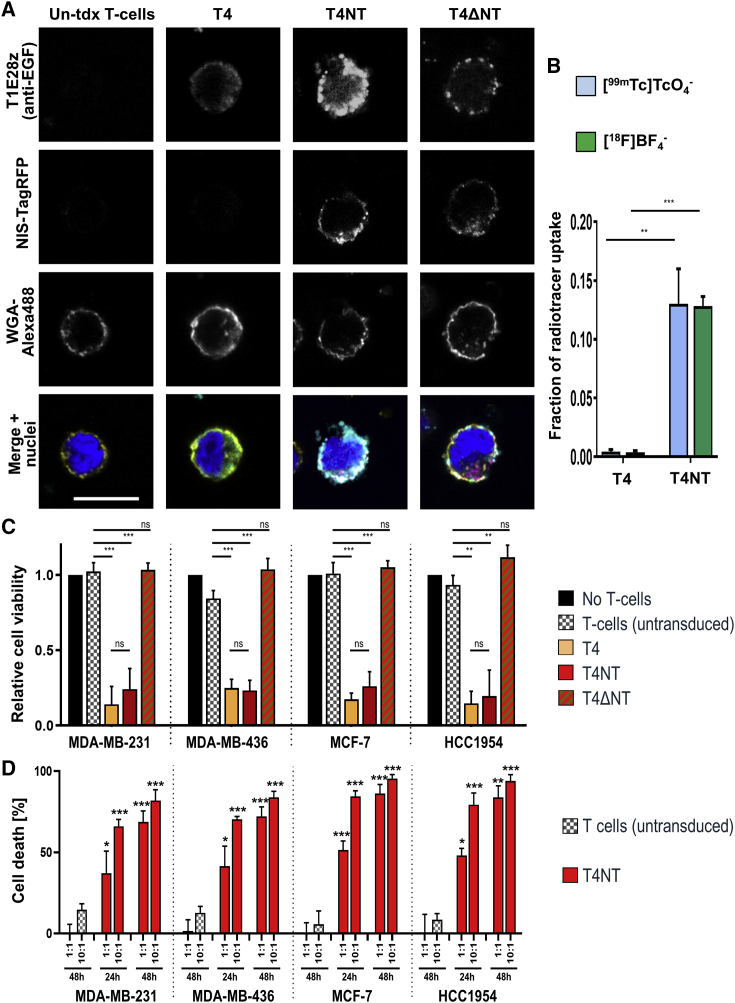
(A) Confocal microscopy demonstrated correct plasma membrane localization of the CAR and the NIS-RFP fusion reporter through co-localization with the plasma membrane marker WGA (conjugated to the fluorophore AlexaFluor488). Typical micrographs are shown; scale bars is 10 μm, image dimensions are identical for all images. (B) NIS-RFP reporter function in T4NT CAR T cells was validated by uptake of either the PET radiotracer [18F]BF4− or the SPECT radiotracer - [99mTc]TcO4−. Uptake was comparable with the two different NIS radiotracers and was 0.13 ± 0.01 and 0.13 ± 0.03, for [18F]BF4− and [99mTc]TcO4− respectively, compared to larger cancer cells overexpressing NIS-RFP,24 which served as experimental reference. CAR T cells lacking the reporter (T4) did not show any radiotracer uptake. Error bars are SD; n = 3 different CAR T cells batches generated from different donors. (C and D) Validation of CAR function by BCC monolayer killing assays. (C) BCC cell viability was assessed after incubation with indicated CAR T cells or T cells alone, as indicated. A negative control (black) was obtained by not adding immune cells. Addition of the reporter NIS-RFP did not impact CAR function (no difference between red and yellow) while dysfunctional CAR (red-brown) and untransduced T cells (gray) did not mediate tumor cell killing. Error bars are SD; n ≥ 3 different CAR T cell batches each. (D) Cell death was determined in the presence of different amounts of either T4NT or untransduced T cells from the same batches (1:1 or 10:1) at the indicated time points. Error bars are SD; n = 3 independent experiments. Significant differences compared to untransduced T cell experiments at same ratios indicated as ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.