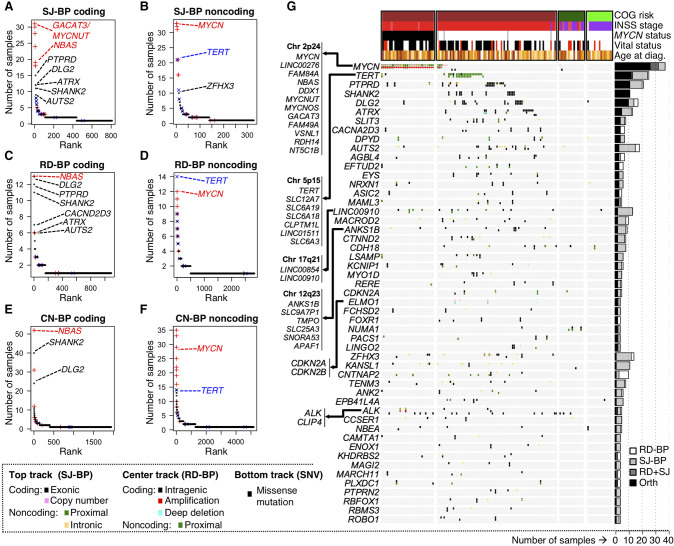
Figure 3.
Identification of recurrently altered genes in neuroblastoma by breakpoint analyses. (A–F) Recurrently altered genes ranked based on different breakpoint analyses and mode of impact: (A) gene coding sequences with recurrent SJ-BPs; (B) gene proximal and intronic sequences with recurrent SJ-BPs; (C) gene proximal sequences with recurrent RD-BPs; (D) gene coding sequences with recurrent RD-BPs; (E) gene coding sequences with recurrent CN-BPs; and (F) gene proximal sequences with recurrent CN-BPs. (G) OncoPrint based on the WGS data set recurrently altered genes by SVs detected through orthogonal approaches (SJ-BP and RD-BP) as depicted in bar plot (right). The oncoPrint aggregates three tracks per gene representing different BP analysis: (upper) SJ-BP; (center) RD-BP; and (lower) recurrent pathogenic SNVs.