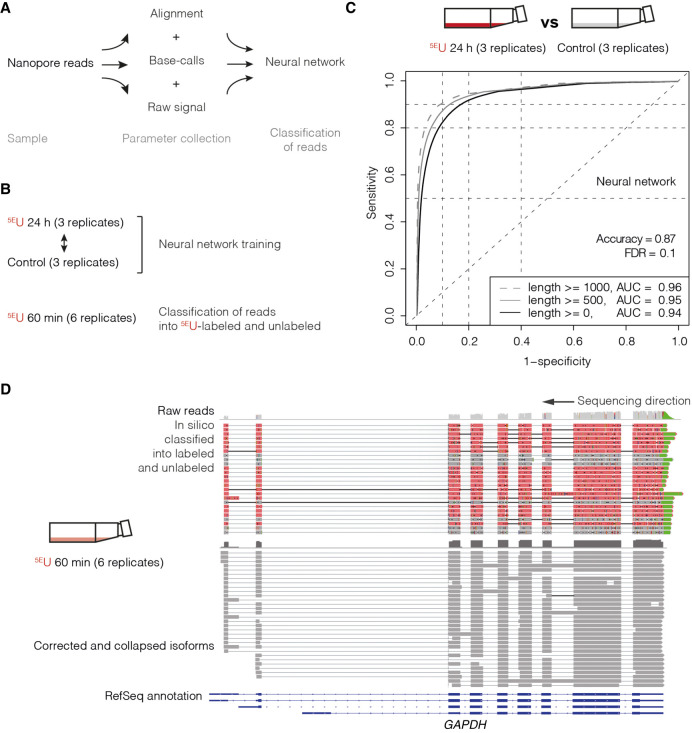
Figure 2.
Direct RNA long-read nanopore sequencing of 5EU-labeled RNA isoforms in human K562 cells. (A) Multilayered data collection scheme. Parameter collection of samples was realized on three different layers: raw signal (electric current), base-call trace values, and alignment-derived mismatch properties (Methods). (B) In this study, data were collected in human K562 cells: control (three replicates) and 5EU 24 h (three replicates), as well as 5EU 60 min (six replicates) (Supplemental Tables S1, S2). The neural network was trained on the 5EU 24 h versus control samples and used to classify reads of the 5EU 60 min samples into 5EU labeled and unlabeled. (C) ROC analysis of fivefold cross-validated neural network training with an accuracy of 0.87 and a false-discovery rate (FDR) of 0.1. Plot shows ROC curves (1 – specificity versus sensitivity) for all reads of the test set (black; alignment length ≥0 nt, AUC = 0.94) (Methods; Supplemental Table S5), for reads with an alignment length >500 nt (gray; alignment length ≥500 nt, AUC = 0.95), and for reads with an alignment length >1000 nt (dashed gray; alignment length ≥1000 nt, AUC = 0.96). (D) Genome browser view of classified direct RNA long-read nanopore sequencing reads of the human GAPDH gene locus on Chromosome 12 (∼8 kbp; Chr12: 6532405–6540375) visualized with the Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV; version 2.4.10; human hg38) (Robinson et al. 2011). From top to bottom, raw nanopore sequencing reads (unlabeled reads are shown in gray, 5EU-labeled reads are shown in red, and poly(A)-tail is shown in green; shown are typical aligned raw reads below the accumulated coverage of all measured reads), and corrected and collapsed isoforms (dark gray) determined with the FLAIR algorithm (Tang et al. 2020) based on raw reads and RefSeq GRCh38 annotation (blue).