Figure 1.
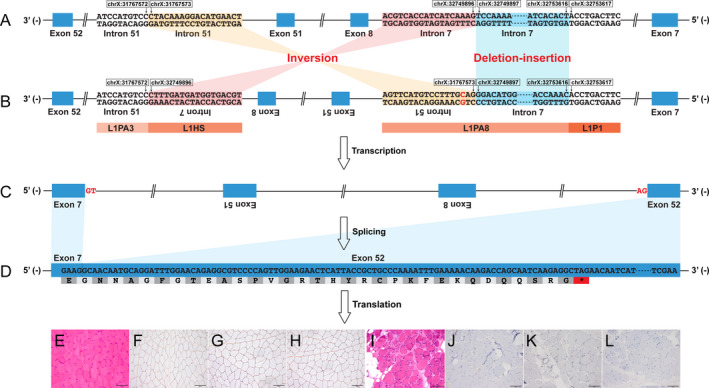
Graphic representation of the aberrant splicing of DMD caused by the complex structural variant. The complex structural variant, 982,323bp inversion flanked by 3,719bp deletion‐insertion, caused the skipping of exons 8–51 from the mature mRNA. The aberrant transcript was predicted to create a frameshift and premature termination codon, which was consistent with the absent expression of dystrophin observed on immunostaining. (A) reference genome; (B) patient genome (NC_000023.10); (C) dystrophin pre‐mRNA; (D) dystrophin mRNA (NM_004006.2). (E) and (I) hematoxylin and eosin staining (×20); (F) and (J) immunohistochemical staining for dystrophin‐N (×20); (G) and (K) dystrophin‐C (×20); (H) and (L) dystrophin‐R (×20). (E)–(H), a healthy control; (I)–(L), the patient. L1, LINE‐1.
