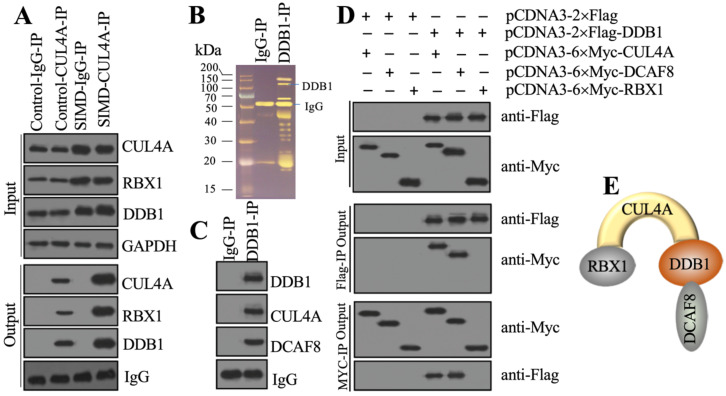
Figure 2.
CUL4A formed a complex with RBX1, DDB1 and DCAF8 in vitro and in vivo. (A) In vivo IP results. Equal weights of heart tissues from three control or SIMD mice were mixed and then lysed in RIPA buffer to isolate total proteins. Total cell extracts were subjected to IP assay using anti-CUL4A-coupled protein A beads. The input and output proteins were used for immunoblotting to examine the protein levels of CUL4A, RBX1 and DDB1. GAPDH and IgG were the loading controls of input and output, respectively. (B) DDB1-associated proteins in vivo. Equal weights of SIMD heart tissues (n=3) were mixed together and lysed in RIPA buffer, followed by IP with IgG (negative control) or anti-DDB1-coupled protein A beads. The purified DDB1-associated protein complex was stained by a silver staining kit. The DDB1 and IgG bands were indicated. (C) DDB1 could pull down DCAF8 in vivo. The IP products used in (B) were applied to immunoblots to detect the protein levels of DDB1, CUL4A and DCAF8. IgG was used as a loading control. (D) Co-IP results. Cells were cotransfected with the plasmid combinations as indicated in the figure, followed by co-IP analyses using anti-Myc-agarose or anti-Flag-agarose beads. The input and output proteins were used to detect protein levels with anti-Flag and anti-Myc antibodies. (E) A representative model of the RBX1-CUL4A-DDB1-DCAF8 protein complex.