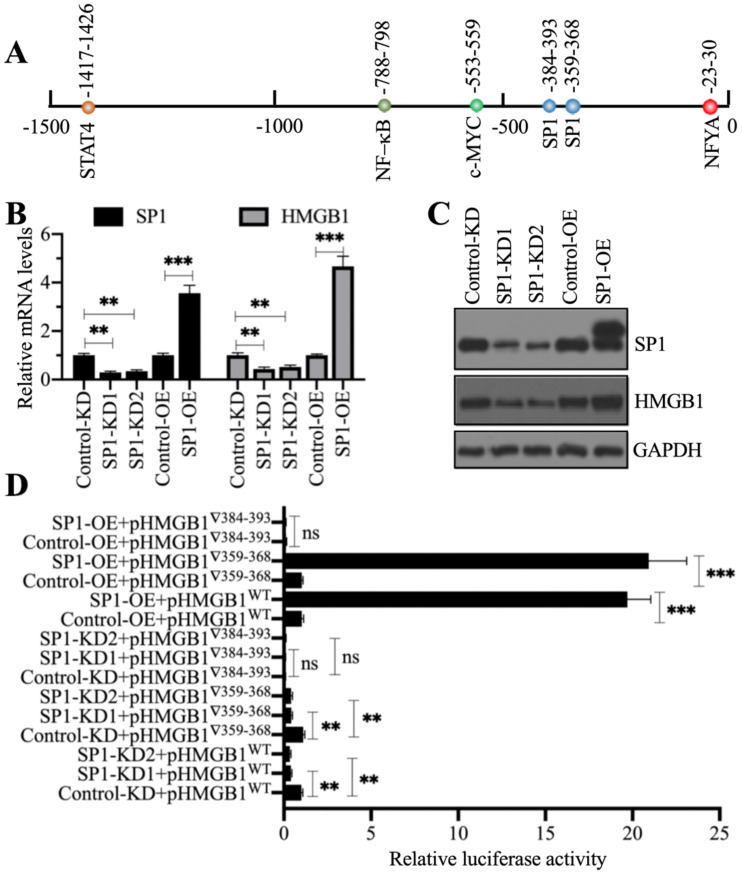
Figure 5.
SP1 specifically regulated the expression of HMGB1. (A) The predicted TF binding sites in the promoter of HMGB1. A 1500-bp fragment of the HMGB1 promoter was selected to predict the potential TF binding sites. One NFYA, two SP1, one c-MYC, one NF-κB, and one STAT4 binding site were identified, and their positions are indicated. (B) The relative mRNA levels of SP1 and HMGB1. Total RNA from Control-KD, SP1-KD (#1 and #2), Control-OE, and SP1-OE cells was used to detect the mRNA levels of SP1 and HMGB1. ** P < 0.01 and *** P < 0.001. (C) The protein levels of SP1 and HMGB1. Total cell extracts from cells used in (B) were subjected to immunoblotting to examine the protein levels of SP1 and HMGB1. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (D) The relative luciferase activity. Cells coexpressing pGL4.26-pHMGB1WT (or pGL4.26-pHMGB1▽359-368 or pGL4.26-pHMGB1▽384-393) and Renilla into were subjected to a dual-luciferase reporter assay. ** P < 0.01 and *** P < 0.001. ns represents no significant difference.