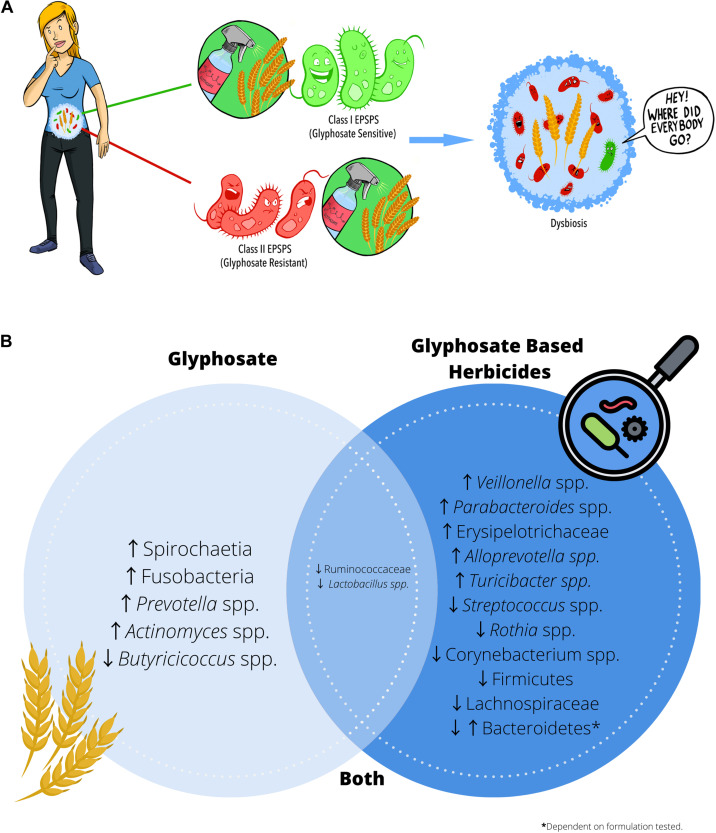
FIGURE 2.
Glyphosate residues present on food may cause intestinal dysbiosis. (A) Glyphosate exhibits its herbicidal action through inhibition of the shikimate pathway enzyme EPSPS. Class I EPSPS are sensitive to the effects of glyphosate and are found in all plants and bacteria. However, glyphosate resistant EPSPS (Class II) appear to be more prevalent in opportunistic pathogens and may contribute to dysbiosis. (B) Summary of the alterations in microbial composition reported in the literature when administering either glyphosate or glyphosate-based herbicides.