Figure 8.
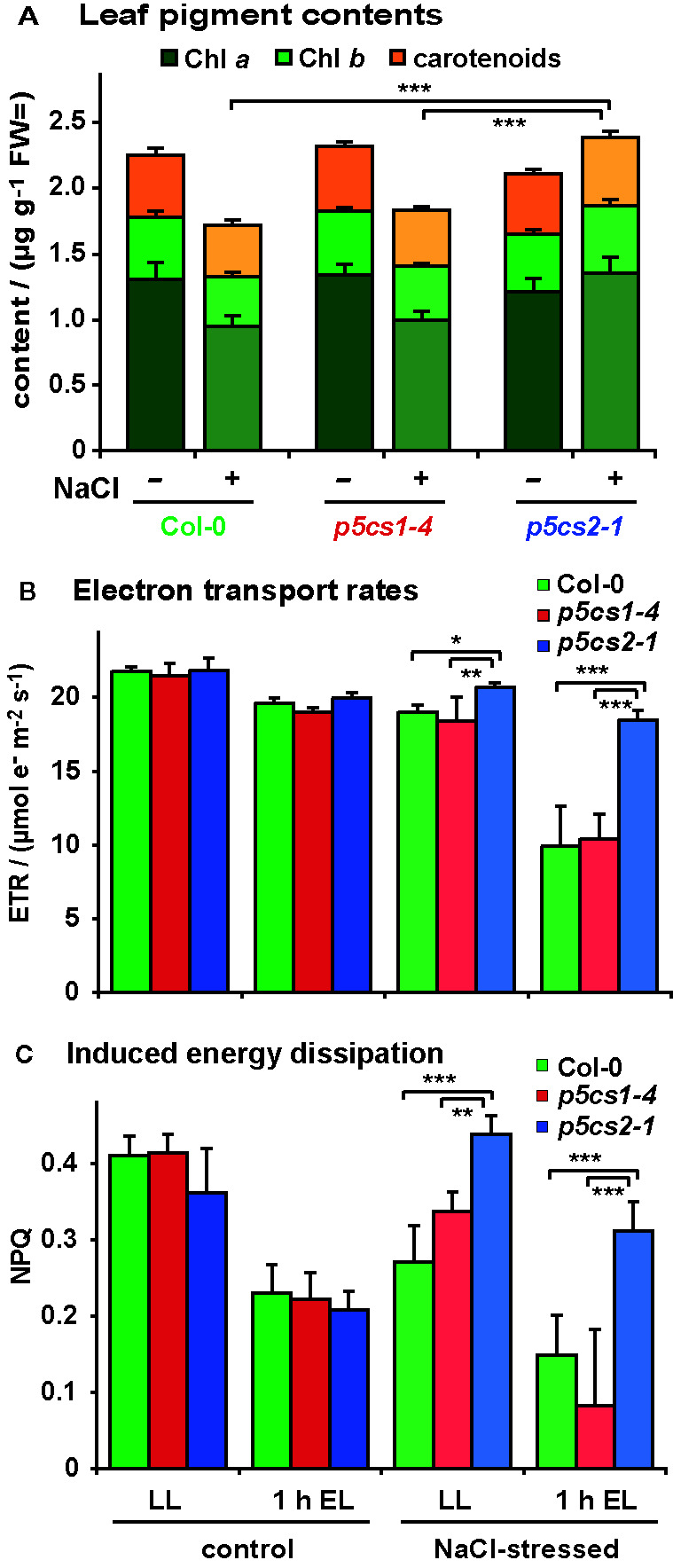
Influence of salt stress and excess light on photosynthetic performance of p5cs1 and p5cs2 mutants. Six-week-old plants were stressed with 300 mM NaCl 4 and 2 days before the analysis. (A) Pigment content of mature leaves. (B) Chlorophyll fluorescence analysis combined with red and near infrared reflection measurements was used to estimate electron transport rates prior to and after 1 h exposure to excess light stress (EL, 1,000 ± 100 µmol photons m−2 s−1). (C) Inducible energy dissipation (NPQ) measured on the same leaves as in (B). Bars represent the average +SD of 4 or 5 replicates per condition and genotype. ANOVA analysis revealed significant differences depending on treatment, genotype and treatment x genotype interaction in all three data sets ( Supplementary Tables S5 , S6 ). Pairwise comparisons showed that NaCl stress caused reduced pigment contents in Col-0 and p5cs1-4 mutants, but increased pigment contents in p5cs2-1 mutants. Both NaCl stress and excess light treatment reduced ETR in all genotypes, but p5cs2-1 mutants were significantly less affected. Inducible energy dissipation (NPQ) was decreased by NaCl stress and excess light treatment in Col-0 and p5cs1-4 mutants, but increased by NaCl stress in p5cs2-1 mutants. Asterisks indicate significant differences between genotypes within one condition (*, **, ***: p < 0.5, < 0.01, and < 0.001, respectively).
