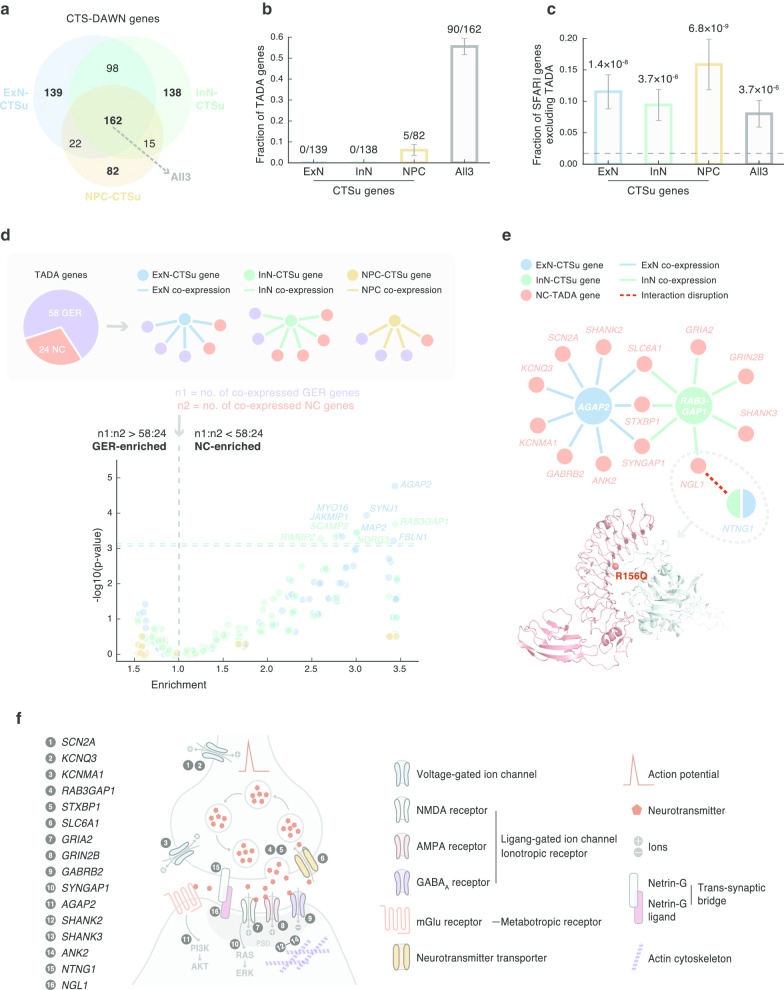
Fig. 5.
CTS co-expression drives the discovery of novel CTS-DAWN genes. a CTS-DAWN identifies genes that are unique to a particular cell type. b Overlaps between CTS-DAWN genes and TADA genes. c Overlaps between CTS-DAWN genes and SFARI genes. TADA genes were excluded from the analysis. Dashed line indicates the fraction of nonsignificant genes in DAWN analysis that overlap with SFARI genes. d CTSu-DAWN genes tend to be co-expressed with TADA genes involved in neuronal communication. Upper: A schematic diagram illustrating the co-expression analysis of CTSu-DAWN genes and TADA genes. Lower: A volcano plot showing the degree to which each CTSu-DAWN gene is GER enriched (left -axis) or NC enriched (right -axis), against corresponding statistical significance on -axis (negative log10(P value)). Horizontal dashed lines indicate the threshold for significance after Bonferroni correction; names of genes that passed the correction are shown. e A condensed NC sub-network formed by inter-connected CTSu-DAWN genes and TADA genes. A co-crystal structure of NGL1-NTNG1 (PDB ID: 3ZYJ) displaying the interface location of an ASD proband dnMis variant NGL1 p.R156Q is shown below. f A schematic diagram showing the distribution and function of NC sub-network genes on neuron structures. The 16 NC sub-network genes function in a range of components of an NC circuit: (1) SCN2A, (2) KCNQ3, and (3) KCNMA1 encode voltage-gated ion channels; (4) RAB3GAP1 and (5) STXBP1 assist neurotransmitter exocytosis, while (6) SLC6A1 promotes restoration; (7) GRIA2 and (8) GRIN2B encode glutamate receptors, and (9) GABRB2 encodes a GABAA receptor; in receptor-mediated pathways, (10) SYNGAP1 suppresses NMDAR-RAS signaling and (11) AGAP2 transmits signals from mGlu receptor to PI3K; in postsynaptic density (PSD), (12) SHANK2, (13) SHANK3, and (14) ANK2 connect membrane receptors to the actin cytoskeleton; (15–16) the NTNG1-NGL1 interaction forms a trans-synaptic bridge. Abbreviations: CTS, cell-type-specific; DAWN, detecting association with networks; CTS-DAWN genes, genes identified by DAWN in specific cell types; ExN, excitatory neurons; InN, inhibitory neurons; NPC, neural progenitor cells; CTSu, cell-type-specific unique; ExN/InN/NPC-CTSu: genes identified uniquely in one cell type; All3, genes identified in all three cell types; TADA, transmission and de novo association; GER, gene expression regulation; NC, neuronal communication; NC-TADA, genes implicated by TADA and affect neuronal communication