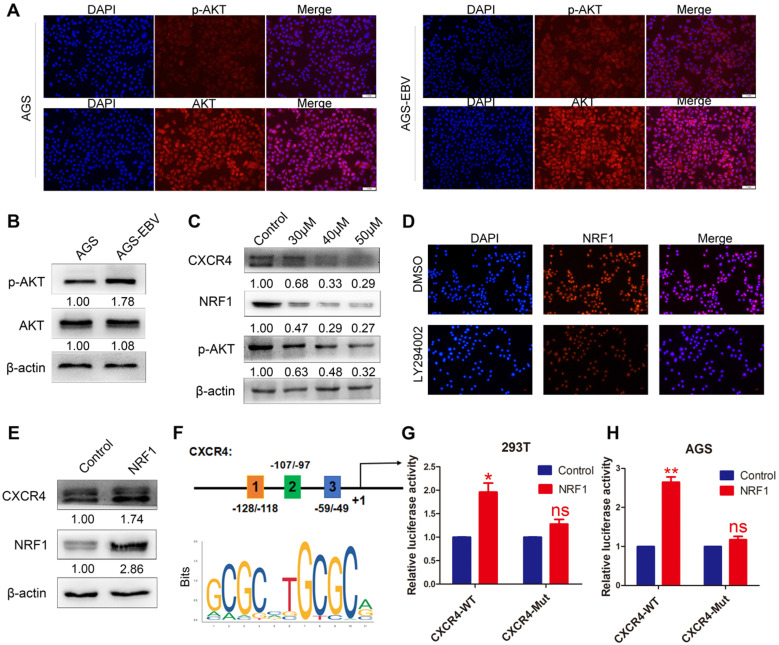
Figure 2.
The effect of PI3K/AKT signalling on CXCR4 expression. (A) Immunofluorescence staining showed the expression and cellular localization of AKT (red) and p-AKT (red). Cell nuclei were visualized by Hoechst 33258 staining (blue). (B) Western blotting was used to detect AKT and p-AKT expression in EBV-associated GC cells. (C) The EBV-positive cell line AGS-EBV was treated with 30 µM, 40 µM and 50 µM LY294002 for 24 h. CXCR4, NRF1 and p-AKT protein levels were analysed using specific antibodies. Cells were treated with DMSO as a control. (D) Expression and location of NRF1 in AGS-EBV cells treated with LY294002 was detected by fluorescence microscopy. (E) Ectopic expression of NRF1 in AGS cells promoted the expression of CXCR4 protein. (F) Binding sites of NRF1 at the CXCR4 promoter and structure of the CXCR4 promoter luciferase reporter construct. The bottom panel is the consensus binding sequence motif of NRF1. (G) CXCR4 promoter activity was detected in 293T cells overexpressing NRF1 using a dual luciferase reporter system. (H) NRF1 activates CXCR4 promoter activity in AGS cells using a dual luciferase reporter system.