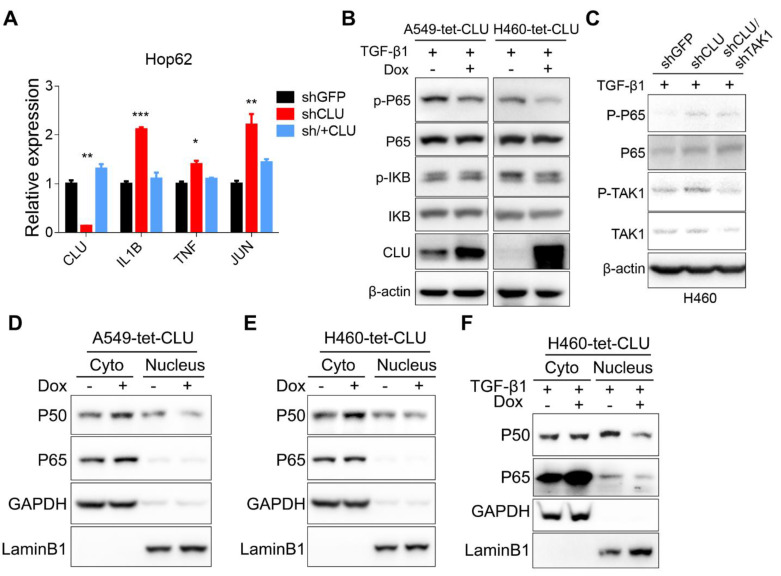
Figure 4.
TAK1-NF-κB pathway mediates growth-promoting effects in CLU-deficient lung cancer cells. (A) RT-PCR evaluation of expression of NF-κB target genes in CLU knockdown or replenished Hop62 cells. Total RNA of engineered Hop62 cells were extracted. Expression of indicated genes was assayed with RT-PCR. (B) Influence of CLU expression on phosphorylation of NF-κB proteins in lung cancer cells. Lung cancer cell lines were treated with TGF-β1 with or without Dox. Total proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE following immunoblotting with antibodies against indicated NF-κB proteins. (C) Western blot evaluating the impact of TAK1 on P65 activation in CLU knockdown cells. Cells were treated with TGF-β1 (5 ng/mL) for 4 h. (D) and (E) Western blot evaluating the impact of CLU on cellular localization of NF-κB proteins. CLU expression in engineered lung cancer cells was induced with Dox. Cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions were separated from the lung cancer cells, followed by western blot with indicated antibodies. (F) Lung cancer cells were treated with TGF-β1 (5 ng/mL) for 2 hours before cytoplasmic and nuclear fraction were separated. Western blot was performed with indicated antibodies. Loading control: GAPDH for cytoplasmic; LaminB1 for nuclear. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.0005, n = 3.