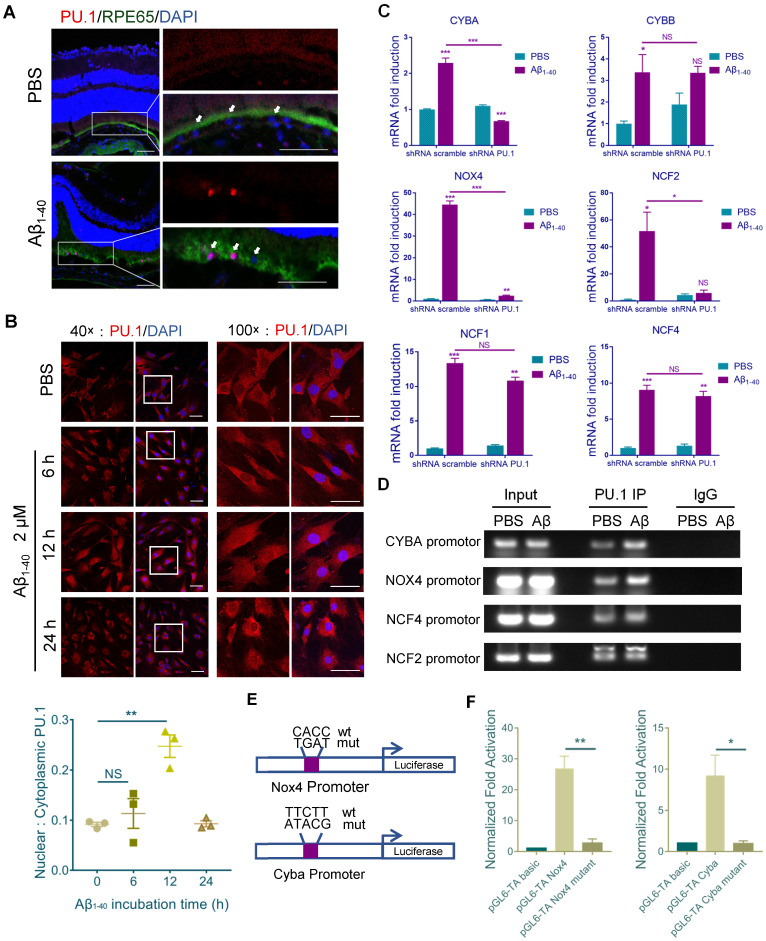
Figure 6.
PU.1 is a key transcriptional regulator of NADPH oxidase. (A) Representative confocal microscopy images of frozen retinal sections for RPE cells (arrows) stained with PU.1 (red) at 4 days post-injection. Scale bar = 50 µm. (B) Immunoreactivity for PU.1 in the nuclei and quantification of nuclei/cytoplasm ratios of PU.1 staining in Aβ1-40-treated primary mouse RPE cells at 0, 6, 12, and 24 h. Images labeled “100×” are magnified portions of the images labeled “40×” (white boxes). Scale bar = 50 µm. (C) Primary mouse RPE cells were transfected with lentivirus carrying scramble shRNA and PU.1 shRNA for 24 h. NADPH oxidase subunit mRNA levels were evaluated by qRT-PCR and standardized to those of a housekeeping gene. (D) ChIP analysis of the association of PU.1 with the CYBA, NOX4, NCF4, NCF2, and CYBB gene promoters was conducted 12 h after Aβ1-40 stimulation. The immunoprecipitated DNA was then analyzed by semiquantitative PCR using promoter-specific PCR primers. Input DNA was used as a normalization control. (E) Schematic diagram representing the binding sites of different gene promoters and corresponding mutants. (F) pGL4-TA vectors containing binding sites for the Cyba and Nox4 promoters were transfected into primary RPE cells. Luciferase activity was measured 12 h after transfection and compared to that in cells transfected with pGL6-TA basic. All data are presented as the mean ± SEM; n = 3 for each group. NS = nonsignificant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, Student's t-test.