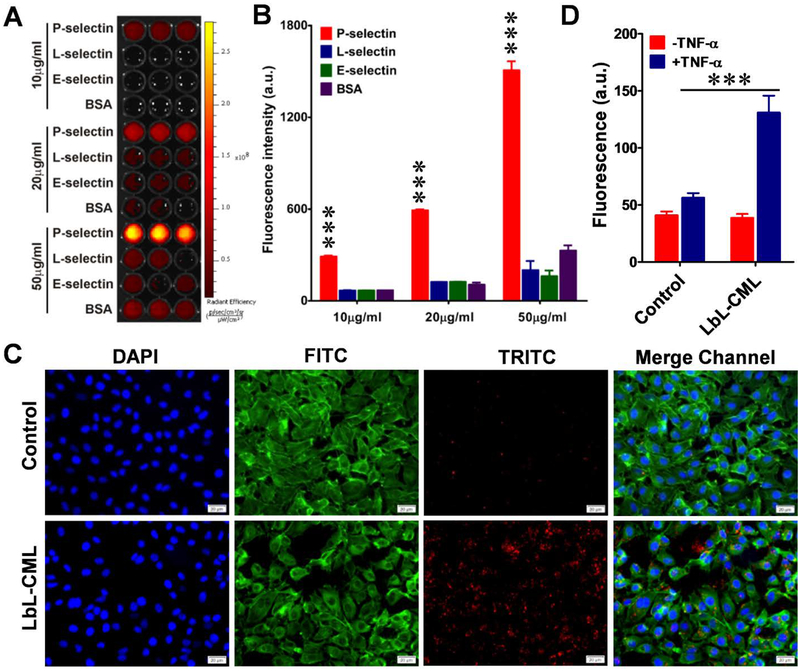
Figure 4. Fucoidan-coated LbL nanoparticles selectively bind to P-selectin and exhibit increased penetration across the endothelial barrier.
A. The binding capacity of fucoidan-functionalized dye (red)-labeled CML beads (LbL-CMLs) to immobilize recombinant P-selectin. Recombinant P-selectin, L-selectin, E-selectin, and BSA at three different concentrations (10, 20 and 50 μg/ml) were immobilized on ELISA plates, which were thoroughly washed and then incubated with dye (red)-labeled LbL-CMLs. Fluorescence was captured with an in vivo imaging system. B. The fluorescence intensity of each well in A was recorded and compared between groups (n=5), ***<0.001. C. Fluorescence images of human endothelial monolayers (EA.hy926 cells) treated with TNF-α to induce the expression of P-selectin, which increased the binding of fucoidan-functionalized LbL-CMLs. Control: cells without TNF-α treatment. Blue channel: DAPI staining of nuclei. FITC channel: fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled phalloidin staining of actin. TRITC channel: dye (red)-labeled LbL-CMLs. Scale bar: 20 μm. D. The LbL-CMLs show high-level penetration through an activated endothelial monolayer barrier, as assessed by transwell assay (n=5), ***<0.001.