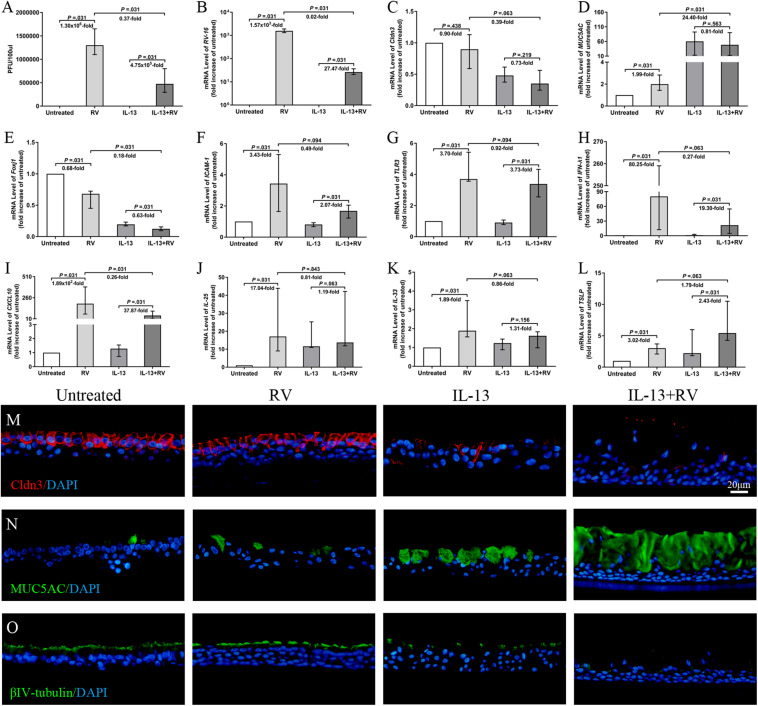
FIGURE 5.
Effects of RV infection on TJs and innate immune response on IL-13-treated hNECs. The RV progeny production and viral RNA expression were significantly increased for both untreated and IL-13-treated hNECs. Extent of RV progeny production and viral RNA expression were significantly lower in IL-13-treated hNECs as compared to untreated hNECs (A,B). RV infection induced trend of reduction of Cldn3 mRNA expression in both IL-13-treated and untreated hNECs (C). RV infection only significantly increased the mRNA expression of MUC5AC in untreated but not in IL-13-treated hNECs. RV downregulated Foxj1 mRNA levels for both untreated and IL-13-treated hNECs. With IL-13 treatment, regulation of mRNA level of MUC5AC and Foxj1 were significantly higher and lower, respectively than in untreated hNECs (D,E). RV infection significantly increased the mRNA expression of RV receptor ICAM-1, pathogen recognition receptor TLR3 and antiviral IFN-λ1 and CXCL10 in both untreated and IL-13-treated hNECs. With IL-13 treatment, upregulation of mRNA level of CXCL10 was significantly lower than in untreated hNECs (F–I). RV infection significantly upregulated mRNA expression of IL-25 and IL-33 for untreated hNECs but not IL-13-treated hNECs (J,K). RV significantly regulated the mRNA expression of TSLP in both untreated and IL-13-treated hNECs (L). IF staining showed that RV infection induced slight decrease in expression of Cldn3 in IL-13-treated hNECs while expression of MUC5AC and βIV-tubulin was, respectively higher and lower in IL-13-treated hNECs with RV infection (M–O). The relative target gene was normalized to 2– ΔCT with RPL13A as a housekeeping gene. Two-tailed unpaired t-test was used to analyzed differences between hNECs with and without IL-13 treatment. Data were presented as median with an interquartile range. Fold change was quantified with reference to untreated hNECs. Scale bar = 20 μm. hNECs, n = 6.