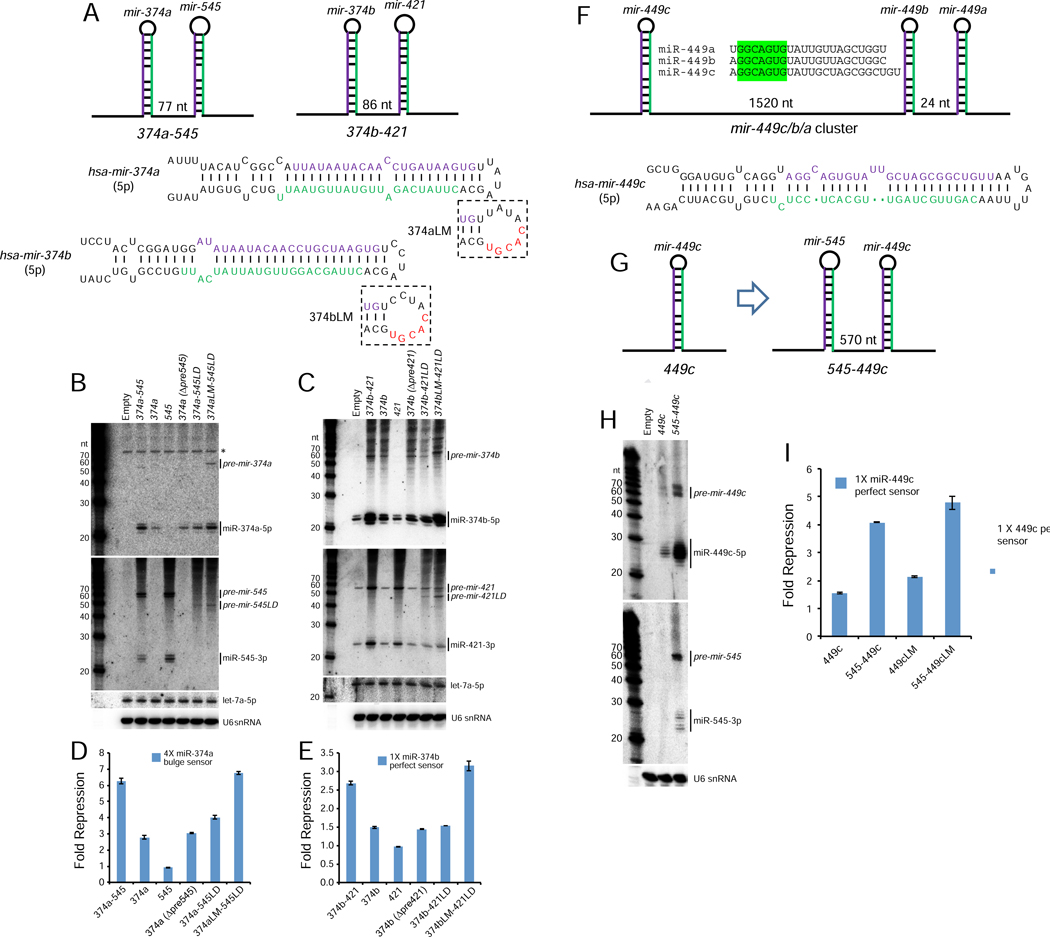
Figure 6. Validation of suboptimal canonical miRNAs whose biogenesis is enhanced within operons.
(A) Schematics of mir-374a/545 and mir-374b/421 clusters, for which mir-374a/b both have 4 nt terminal loops. Also shown are mir-374a/b variants with enlarged terminal loops (LM), which were engineered into cluster constructs in which their partner miRNA carried a loop deletion to inhibit processing (545LD or 421LD). (B, C) Processing of wt and variant mir-374a/545 constructs (B) and mir-374b/421 constructs (C) in HEK293T cells. Note these cells lack miR-374a/miR-545, but do express miR-374b/miR-421; asterisk indicates blots indicates background band hybridized to miR-374a probe. (D, E) Activity of mir-374a (D) or mir-374b (E) from wt and mutated constructs. These assays demonstrate that biogenesis and activity of miR-374a and miR-374b require their miRNA neighbors, but can be compensated by enlarging their terminal loops. (F) Schematic of mir-449c/b/a cluster, which yields three similar mature miRNAs; only mir-449c bears a small (5 nt) terminal loop. (G) To avoid cross-hybridization, we compared the properties of solo mir-449c with an artificial cluster with mir-545. (H) Biogenesis and (I) activity of mir-449c is enhanced when transcribed from an operon relative to a solo context.