Extended Data Fig. 3 |. MCP interactions.
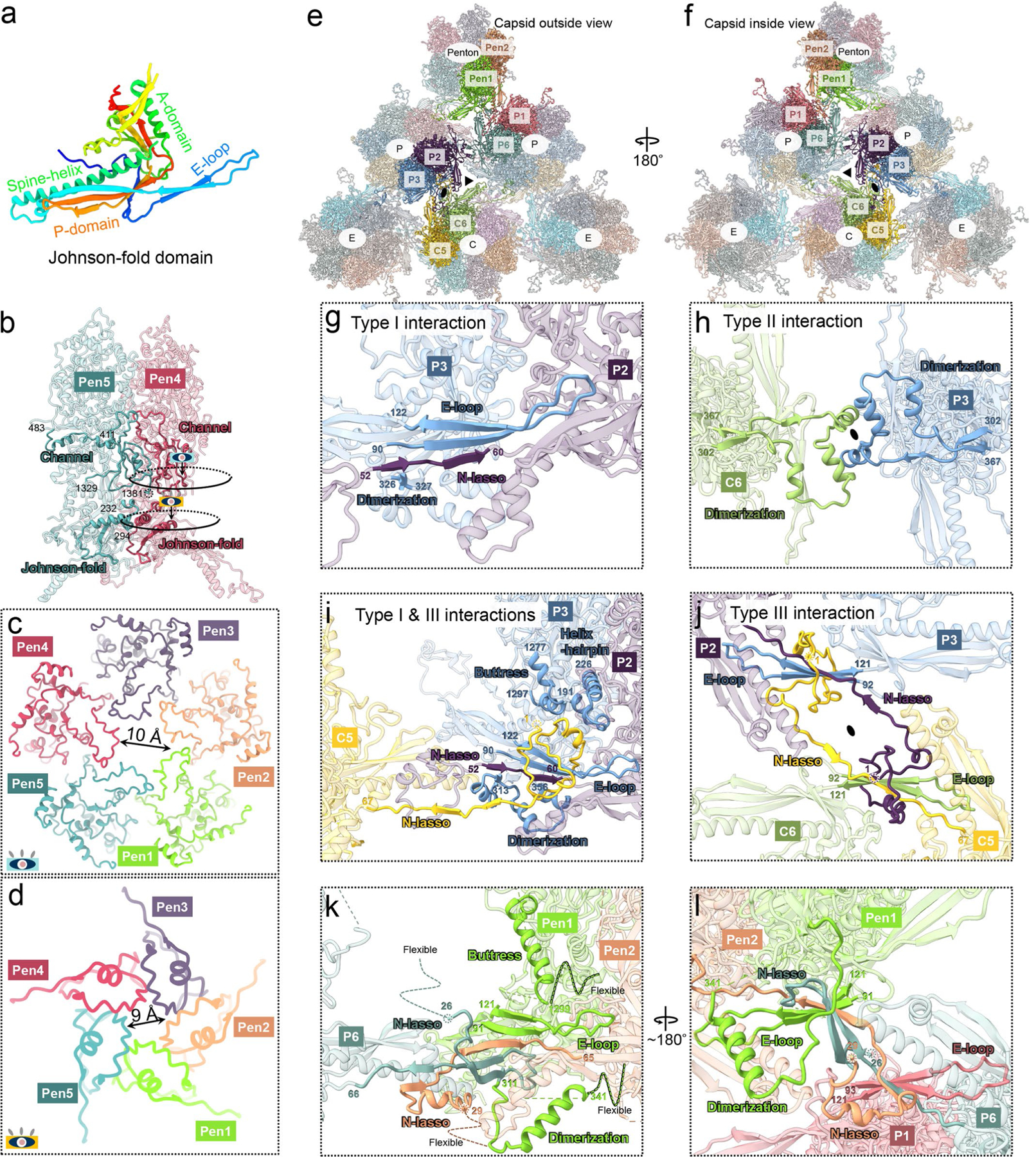
a, Atomic model of the Johnson-fold domain of MCP shown in rainbow-colored ribbon. b-d, MCP-MCP interactions in penton (b) and constrictions in penton channel (c, d). The colored eye symbols in (b) indicate the view directions in (c) and (d). e, f, Part of the MCP network viewed from outside (e) and inside (f) the capsid. g-j, Three types of network interactions among hexon MCPs. Type I interactions (g) are hydrogen bonds in an intra-capsomeric augmentation of β-strands from adjacent MCPs (for example, P2 and P3) in the same capsomer. Type II interactions h, inter-capsomeric interactions among a pair of MCPs (for example, P3 and C6), join two dimerization domains. Type III interactions i, j, characterized by the lassoing action of the N-lasso domain (for example, P3, C5, and C6) among three MCPs, build on and fortify type I interactions (j). k, l, Penton MCP interactions with hexon MCP subunits P1 and P6. Note that penton MCP lacks type II and III interactions and the N-lasso domain of P6 hexon MCP differs from those in other hexon MCPs.
