Figure 4.
Structural Comparison of the Ribosome from Two Different Strains of A. baumannii
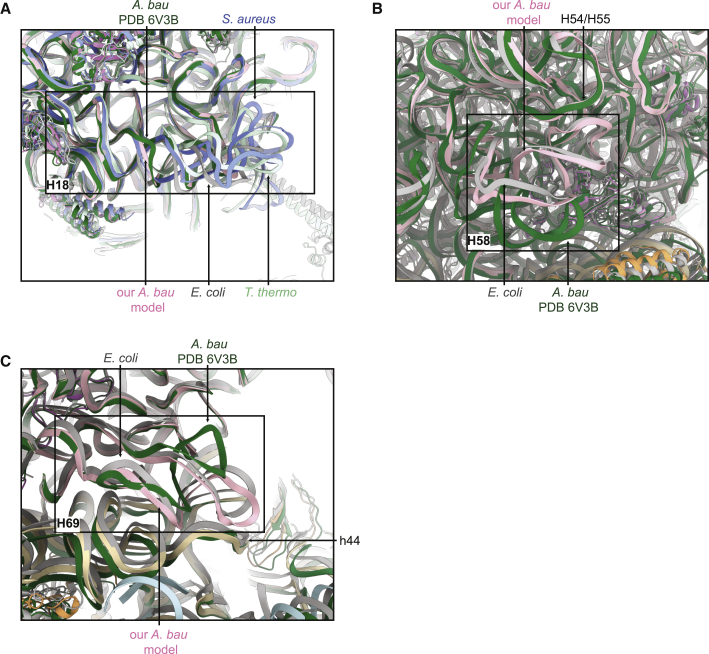
(A) H18 takes up different conformations in A. baumannii (pink, our model; dark green, PDB: 6V3B), E. coli (gray, PDB: 4YBB), S. aureus (blue, PDB: 5LI0), and T. thermophilus (light green, PDB: 5E81).
(B) H58 bends to interact with H54/H55 in our model of the A. baumannii ribosome (pink, strain ATCC 19606) and the E. coli ribosome (gray, PDB: 4YBB), but not in a different A. baumannii ribosome (dark green, strain AB0057, PDB: 6V3B).
(C) H69 reaches toward the 30S subunit to interact with h44 in our model of the A. baumannii ribosome (pink, strain ATCC 19606) and the E. coli ribosome (gray, PDB: 4YBB), but instead bends back toward the 50S subunit in a different A. baumannii ribosome (dark green, strain AB0057, PDB: 6V3B).
The structure of the A. baumannii ribosome-amikacin complex is used to describe the ATCC 19606 A. baumannii ribosome, but the structures of all highlighted regions hold true for the A. baumannii ribosome-tigecycline complex.
See also Figure S6.