Fig. 3.
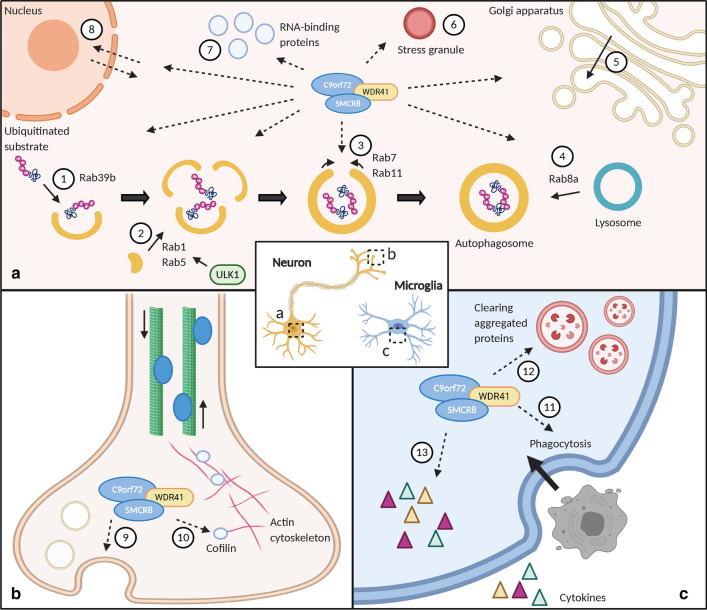
The function of C9orf72 in the central nervous system. a In neurons, C9orf72 (or tripartite complex C9orf72/SMCR8/WDR41) directly or indirectly regulates autophagy at four levels; recruitment of substrates to the phagophore (1), phagophore formation (2), maturation and closure of the autophagosome (3) and fusion of the autophagosome with lysosomes (4). Vesicle trafficking in the Golgi apparatus could also be controlled by C9orf72 (5). Interaction with stress granules (6), RNA binding proteins (7) and nucleocytoplasmic transport factors (8) points towards a possible regulating role of C9orf72 in phase separation (6), RNA metabolism (7) and nucleocytoplasmic transport (8). b C9orf72 also localizes presynaptically where it might interact with extracellular vesicle secretion (9) and the cytoskeleton (i.e. cofilin) (10). c In microglia, phagocytosis of dying neurons and other cells has been associated with C9orf72/SMCR8/WDR41 (11). C9orf72 is involved in the clearing of aggregated proteins (12) and the release of cytokines (13)