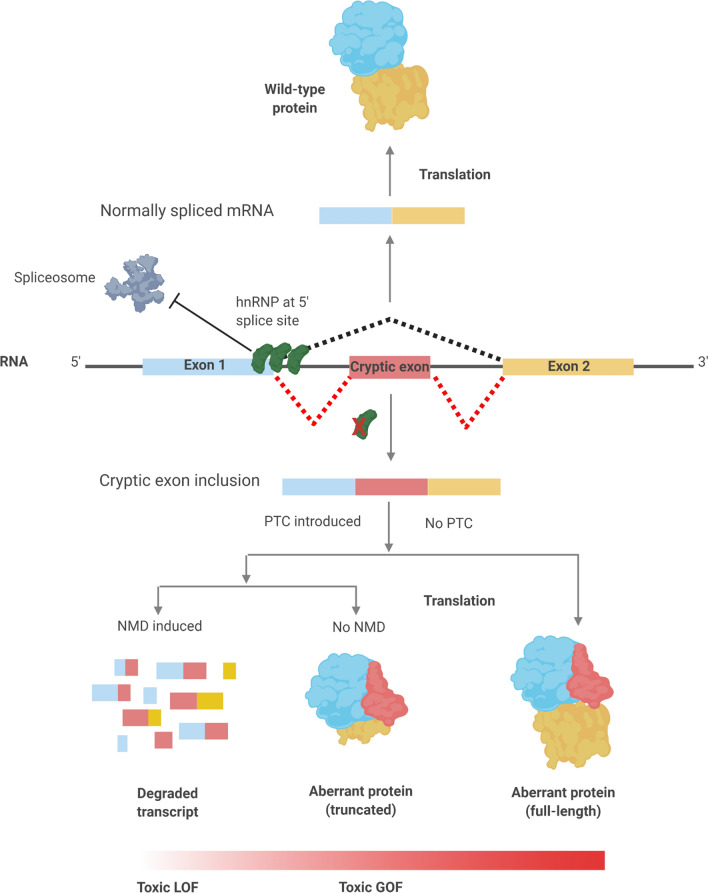
Fig. 3.
HnRNP involvement in cryptic exon repression. Several hnRNP proteins have been known to bind to exonic and intronic regions of pseudo/cryptic 5′ splice sites. Their presence sterically occludes appropriate assembly of the spliceosome, in-turn inhibiting cryptic exon inclusion. HnRNP dysfunction leads to elevated cryptic inclusion in the final mRNA transcript. If a premature termination codon (PTC) is introduced following a frameshift, non-sense mediated decay (NMD) may be activated to destroy the transcript. Alternatively, the transcript may be partially translated into a truncated, aberrant protein isoform. Indeed, if by chance no PTC is introduced upon cryptic splicing then the full-length transcript may be translated